What organism can grow up to 35 inches in a day, conduct electricity, and survive an atomic bomb?
Bamboo!

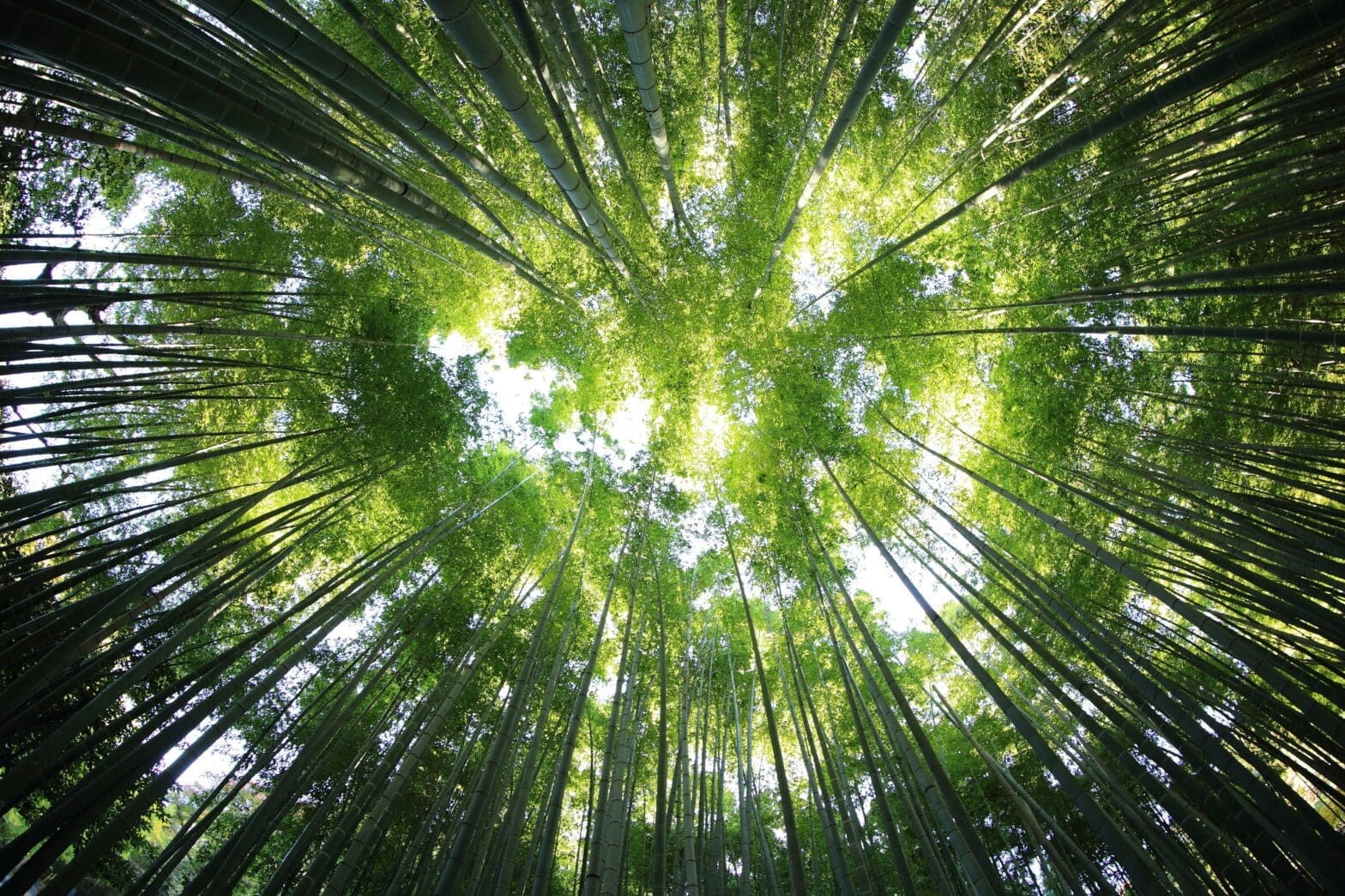
With over 1,600 species of bamboo worldwide, this subfamily (Bambusidae) has a great deal of diversity, and well-earned acclaim. These plants are actually the largest grasses, or members of the family Poaceae.
This talented family boasts a remarkable diversity, with bamboo species native to every continent besides Antarctica and Europe. People and cultures across the world have come to prize bamboo for its amazing growth rates, its extraordinary flexibility and strength, and its ecological contributions to clean air, soil, and water. Whether as a symbol of luck and fortune, a provider of adaptable materials, or an ecosystem restoration MVP, bamboo reminds us of nature’s incredible ability to captivate and nurture.

The word “bamboo” is thought to originate in the Malay word “mambu.” During the late 16th century, the Dutch adopted the term and coined their own version, “bamboes,” which eventually became the “bamboo” we know and love today.
One great grower
Bamboo holds the crown for being the fastest-growing plant on Earth. Some species can achieve astonishing growth rates of up to 90 centimeters (35 inches) in just 24 hours. While giant sea kelp (actually an algae) can surpass bamboo’s growth rates in ideal conditions, the rapid growth of bamboo remains unparalleled among vegetation and land-based photosynthesizers.
Another of bamboo’s most notable qualities is its ability to be harvested without uprooting the plant. This feature allows for comparatively sustainable manufacturing processes, as bamboo regenerates quickly from its robust root system and does not require its rhizomes to be replanted.

A pretty prolific plant
Over centuries, people have found uses for bamboo in various industries, such as construction, furniture, textiles, and paper, and in the present day many are looking to bamboo for greener alternatives to traditional materials. You might see this trend taking off in the latest utensils, toothbrushes, or toilet papers hitting the market, but experiments using these plants are no new fad.
One of the most famous examples of bamboo taking a central stage in innovation came in 1880, when Thomas Edison used carbonized bamboo fiber to conduct electrical current through a lightbulb. After testing a wide variety of materials, he found the bamboo fiber to perform the best, lasting 1,200 hours as the conductor.

Bamboo is particularly renowned for its unique combination of flexibility and strength. This exceptional quality has made it a popular choice in construction. Notably, in Sichuan, China, a thousand-year-old bridge made of bamboo stands as a testament to the plant’s durability. The bridge is still in use today with ongoing maintenance, showcasing the long-lasting potential of bamboo.
People have naturally turned to bamboo for some of our most fundamental activities, like creating shelter, harvesting firewood, making clothing and home goods, and of course, eating. Bamboo shoots are featured in dishes across Asia, while its sap, seeds, leaves, and even the hollow stalks can be used in cooking or fermentation processes. Bamboo textiles offer durability, hypoallergenic properties, natural cooling, and moisture-wicking capabilities, making them ideal for bedding and clothing. Bamboo has also been used to create paper, writing implements, musical instruments, weapons, fishing and aquaculture equipment, baskets, firecrackers, medicine, and more. Truly, what can’t this plant do?

(Photo by Ramon F. Velasquez, CC by 3.0)
An asset to the ecosystem
While humans have found many ways to work with harvested bamboo, I think these amazing grasses are most impressive as living organisms in their environment. Bamboo plays a vital ecological role in its surroundings, working to regulate intact ecosystems and repair degraded ones.
Bamboo’s extensive root system helps control soil erosion, preventing the loss of vital topsoil and providing stability to sloped areas and river systems. Some bamboo species are able to stabilize and hold in place up to six cubic meters of soil with their long roots. Additionally, bamboo can be extremely effective at absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. In particular, “clumping” types of bamboo that grow thickly in dense clusters can filter air up to 30% more effectively than other plants.

(Photo by Maya Dutta)
Bamboo thrives in diverse environments, from tropical to high-altitude regions. It demonstrates exceptional resilience, withstanding extreme cold below -20°C (-4°F) in the Andes and Himalayas and heat up to 50°C (122°F). Notably, bamboo groves were the only plant life to survive the atomic bombings in Hiroshima, Japan, in 1945, and were among the first to resprout after the devastation.
Some species of bamboo are able to survive and thrive even in areas of high pollution, making them an extremely important ally in remediation efforts to remove heavy metals or other toxic substances from soil or wastewater. As a result of these advantages, many people have introduced bamboo species outside of their native areas. In doing so, it is essential to be aware of the potential for displacing vegetation important to local wildlife.
Some bamboo that clusters densely can easily crowd out competition, while other bamboo species can produce allelopathic compounds (natural herbicides) that prevent other plants from growing. In any interventions we make, especially for the good of our environments, a comprehensive systems approach is key. Understanding the elements of an ecosystem and the dynamics that make it function, as well as what outcomes you want to bring about, can help prevent single-minded solutions and unintended consequences that harm biodiversity and ecosystem function in the long run.

Strength in symbolism
Given its history of cultivation that dates back around 6000 years, it is unsurprising that Bamboo holds deep symbolic significance in cultures around the world. In China, it represents various values, including fairness, beauty, virtue, and strength. Its tall, upright growth is associated with integrity and the ability to adapt to challenging circumstances. In India, bamboo is considered a symbol of friendship and enlightenment, embodying qualities of unity and harmony.
One myth with several variants around Asia tells us that humanity emerged from a bamboo stem. If that is the case, then we are coming back to our roots. Let us embrace all this might mean for us — flexibility, fairness, adaptability, strength, and, of course, our interdependence with the biodiverse wonders of this world.
Rooted in admiration,
Maya

Maya Dutta is an environmental advocate and ecosystem restorer working to spread understanding on the key role of biodiversity in shaping the climate and the water, carbon, nutrient and energy cycles we rely on. She is passionate about climate change adaptation and mitigation and the ways that community-led ecosystem restoration can fight global climate change while improving the livelihood and equity of human communities. Having grown up in New York City and lived in cities all her life, Maya is interested in creating more natural infrastructure, biodiversity, and access to nature and ecological connection in urban areas.
Sources and Further Reading:
https://www.bamboodownunder.com.au/20-fun-facts-about-bamboo
https://thebamboopillow.co.uk/50-amazing-bamboo-facts/
https://extension.tennessee.edu/publications/documents/W220.pdf
https://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-0213/ijsrp-p14122.pdf
https://medium.com/@zippyfacts/which-bridge-in-china-has-to-be-tuned-7976a631136a
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bamboo
https://earthbound.report/2019/08/28/using-bamboo-for-land-restoration/
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/bamboo-mathematicians
https://www.dezeen.com/2021/08/04/impressive-bamboo-building-roundup/#