What handsome creature dyes its feathers and almost exclusively eats bones?
The bearded vulture!

The bearded vulture (Gypaetus Barbatus) is a bird of prey known by many names including lammergeier, quebrantahuesos, boanbrüchl, and ossifrage.
The origin of these monikers come from the bird’s unique diet – bones. While most vultures pick off the meat on a carcass, the bearded vulture prefers to consume the skeleton itself. Over 80% of their diet consists solely of bones.
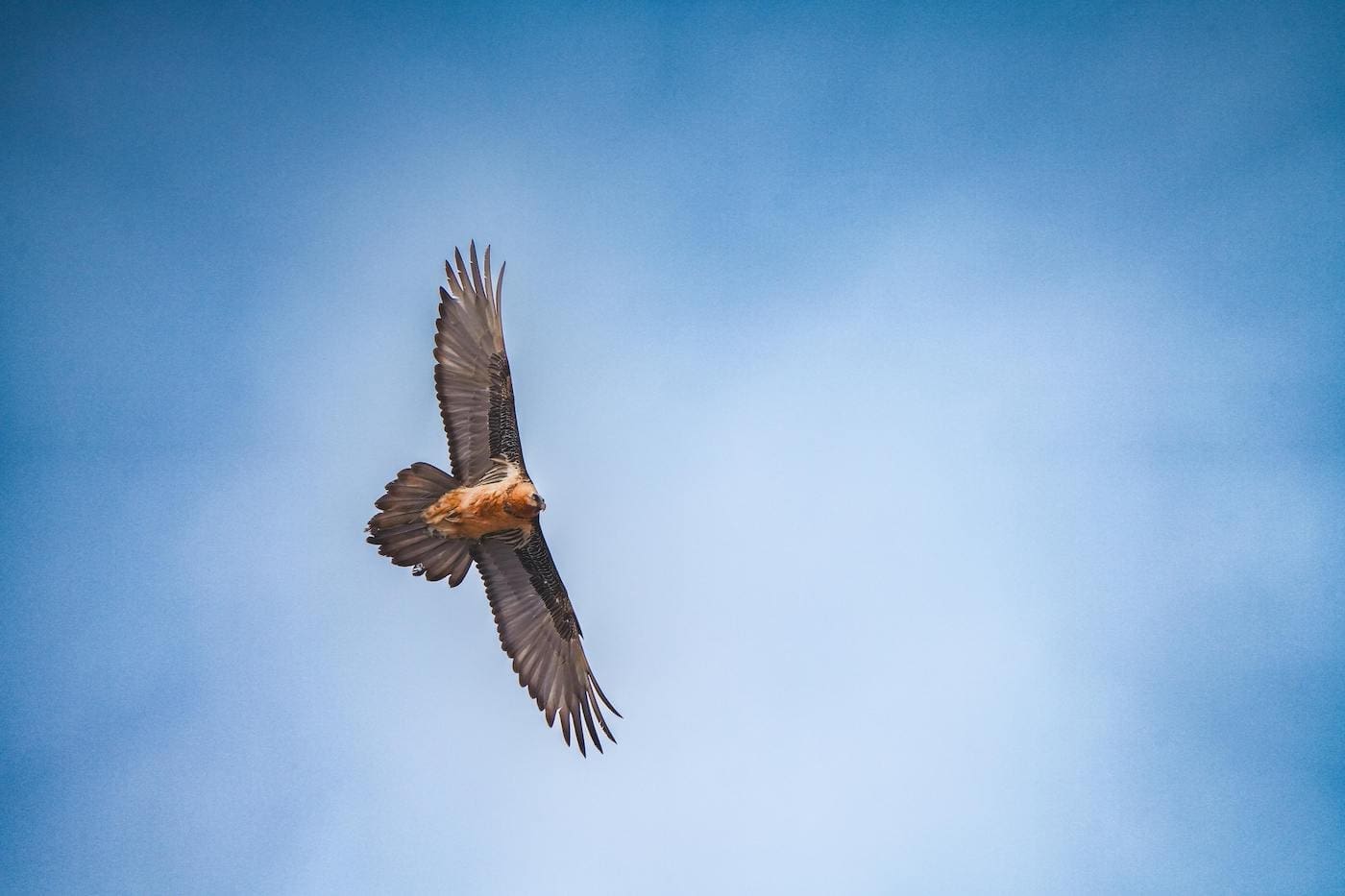
Weighing in at about 16 pounds and equipped with a wingspan of over 9 feet, bearded vultures are among the top ten largest birds of prey in the world. They use their substantial size to hoist the bone of their choice from the skeleton to the sky. They fly high enough to drop it onto a clifftop or boulder to break the bone into smaller, bite-sized pieces which they then swallow whole.
What makes these birds capable of digesting bone is the strength of their stomach acid. Bearded vultures have a stomach acid of nearly zero pH. This extreme acidity dissolves bone within 24 hours. To put this in perspective, humans have a stomach acid pH of about 2 while battery acid has a pH of about 0.8. Bearded vultures are the only carnivores capable of completely digesting bone.

Striking Appearance
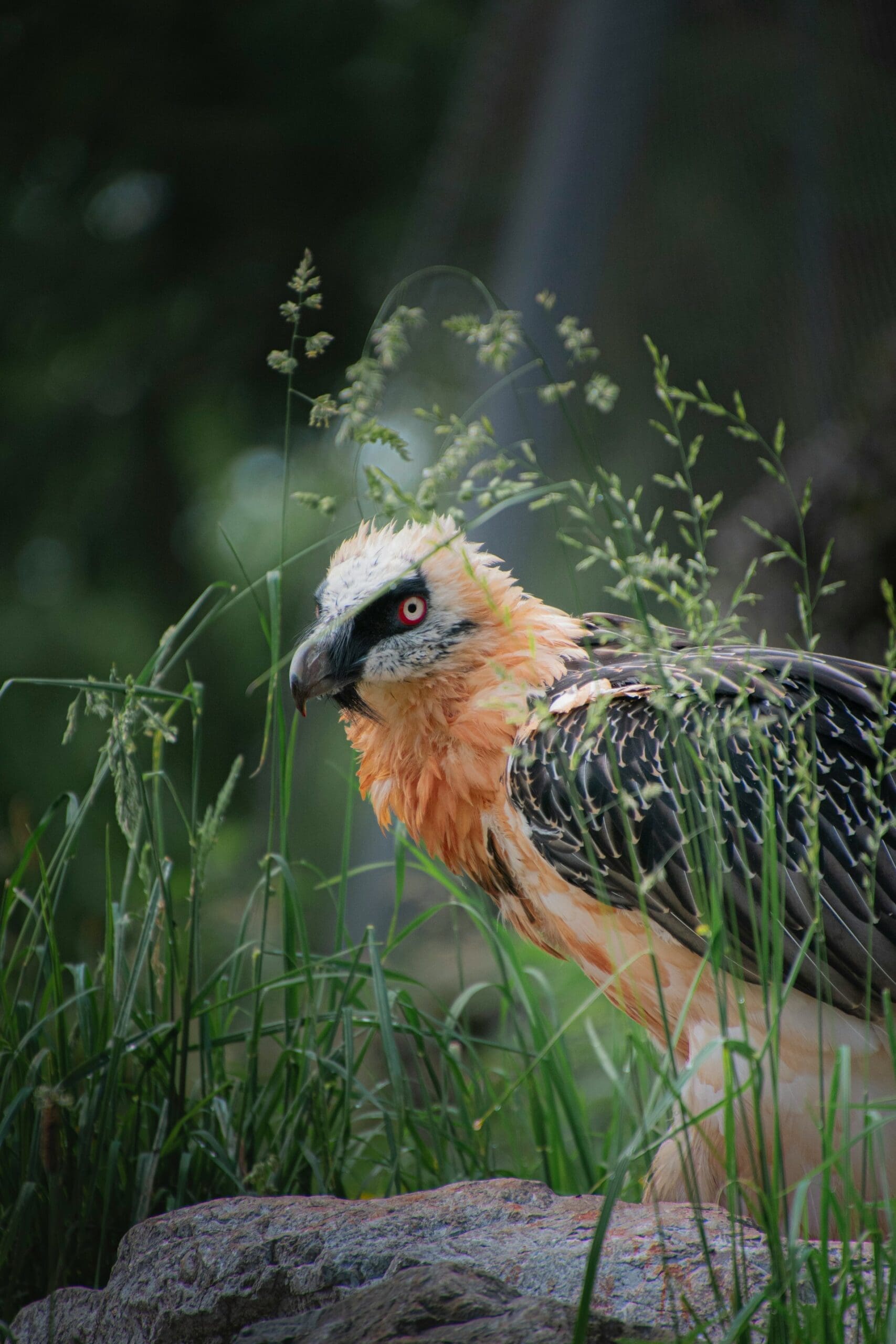
Bearded vultures appear different from most other vultures due to the lack of a bald head. Most vultures are known for having no feathers around their head and neck which helps them remain clean when scavenging carrion. Bearded vultures, because of their chosen bone-based diet, do not need this adaptation, and sport a feathered head. Adults have white feathers along their body, chest, and face while their wings are dark brown. Black tufts protrude from their chin which gives them their modern namesake of bearded vulture.
Bearded vultures have large, glacier-white eyes that help them spot carcasses from the sky. As Old World vultures, their sense of smell is not advanced and they rely primarily on their eyesight when scavenging. When threatened or excited, the scleral ring around their eyes turns a bright red.
Bearded vultures have a unique propensity for the color red, so much so that they dye their white feathers a rusty vermilion. These birds will seek iron-oxide rich pools of muddy water or dust and bathe in it to color themselves a red-orange hue. Researchers are unsure of why they do this. Some posit that it is a sign of status – the redder the bird, the higher the seniority. Others believe the iron-oxide coloring helps prevent infections when breeding. Whatever the reason, bearded vultures paint themselves into a real-life phoenix.

Habitat and Ecological Role
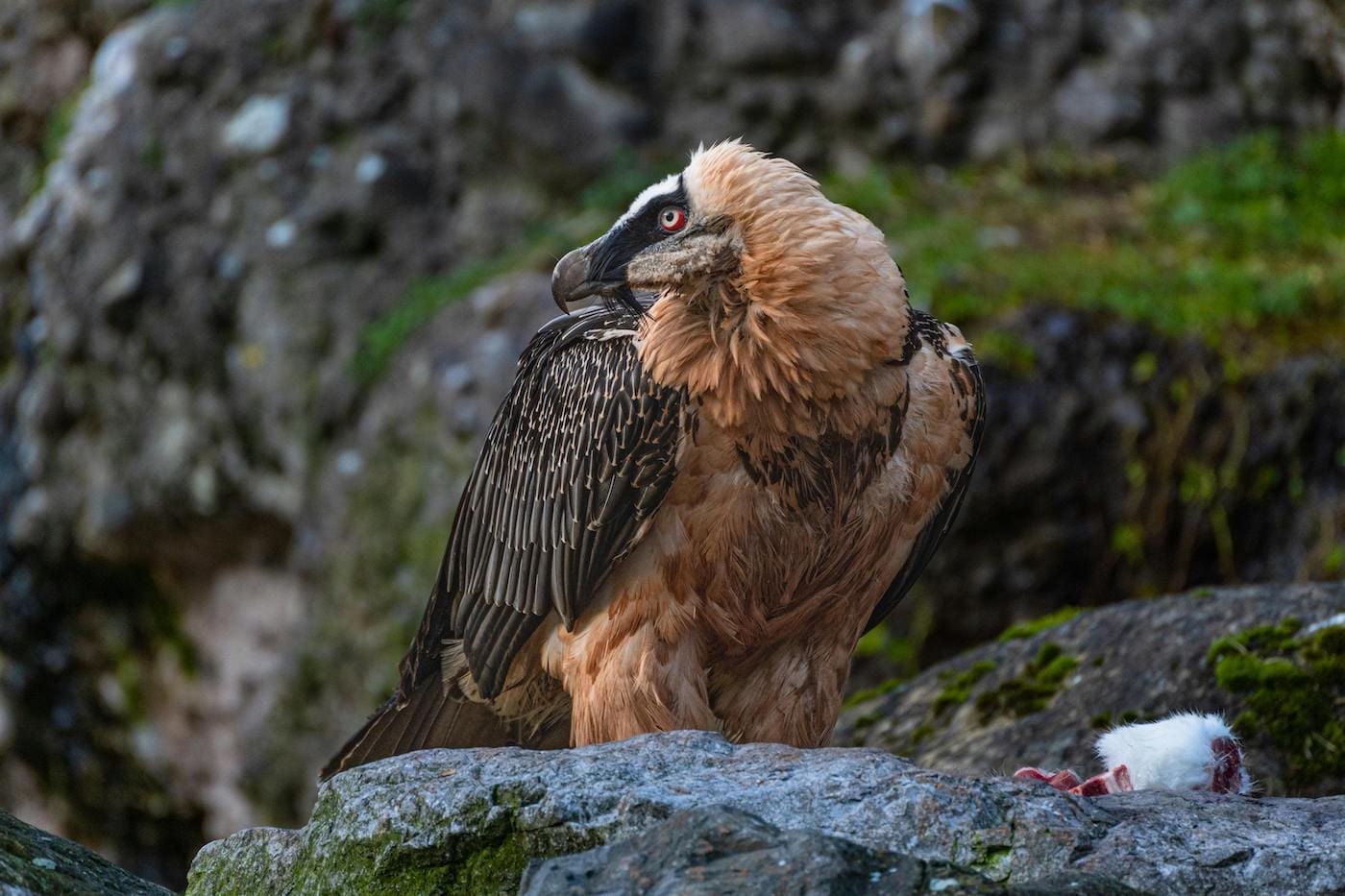
Bearded vultures call the mountainous regions of Eurasia, East Africa, and parts of the Middle East their home. They prefer to live in areas that grant them the best visibility such as remote mountain ranges, steppes, canyons, and alpine valleys.
These birds tend to fly at high altitudes of about 6,500 feet above sea level. They utilize updrafts to ride the air currents which helps them conserve energy and glide for many miles.
In the early 1900s bearded vultures were hunted in Europe due to a false myth that they supposedly preyed upon children and livestock. The population in this area declined and is still recovering today. Currently, humans are the greatest threat to bearded vultures as habitat loss and poisoning endanger the remaining populations. The species is listed as near threatened by the IUCN.
Bearded vultures are an incredibly important species for the ecosystem because they act as nature’s garbage disposal. They help clean the environment of carcasses and diseases which keeps other species healthy.
Soaring away for now,
Joely

Joely Hart is a wildlife enthusiast writing to inspire curiosity about Earth’s creatures. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in creative writing from the University of Central Florida and has a special interest in obscure, lesser-known species.
Sources and Further Reading:
https://www.beardedvulture.ch/beardedvulture/biology
https://faunafocus.com/portfolio/bearded-vulture
https://safarisafricana.com/largest-birds-of-prey
https://factanimal.com/bearded-vulture/
https://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/64406/4/functilife.pdf
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36596809