What creature is the engine of the Portuguese economy and works hard to delight wine-lovers around the world?
The Cork Oak!
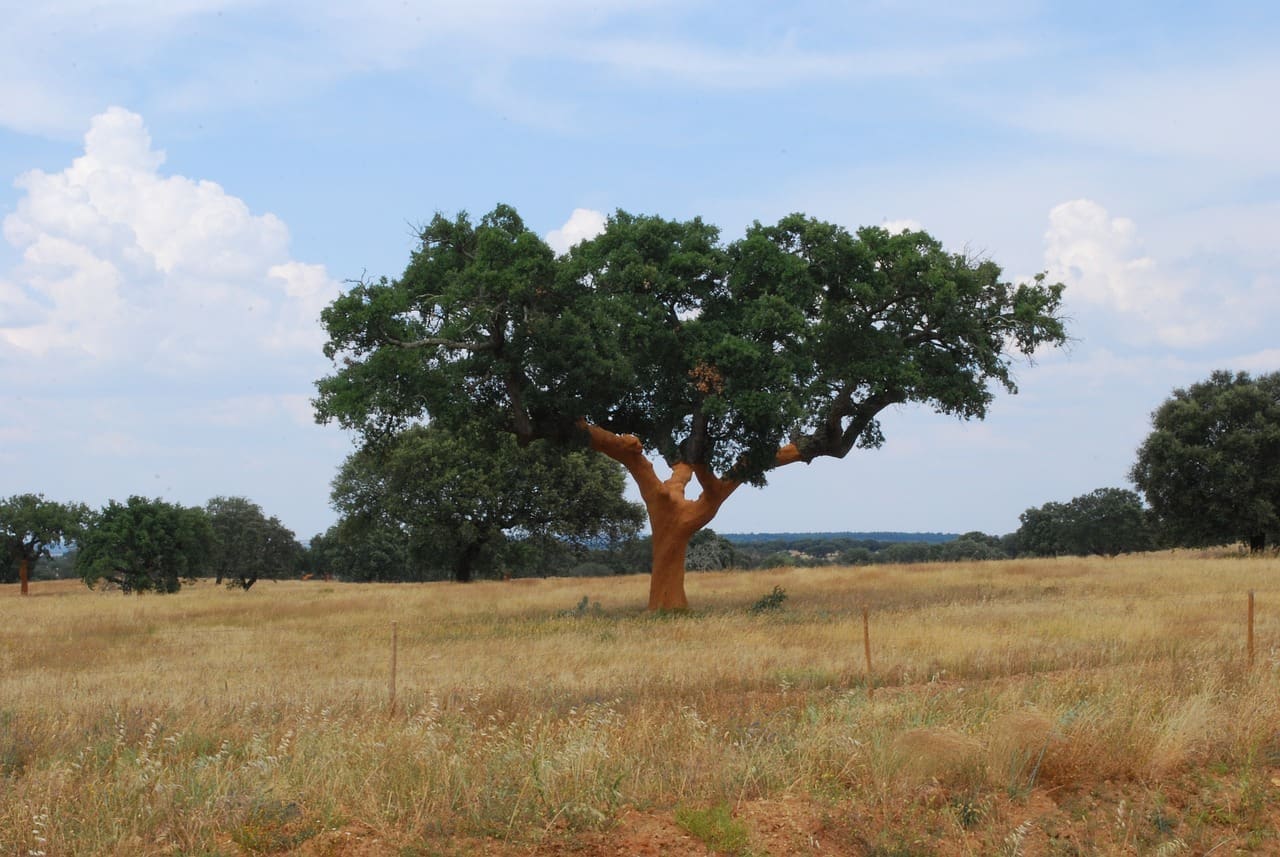

The Cork Oak is a unique tree species whose bark is an ancient renewable and biodynamic material that supports a valuable Portuguese industry. Portugal produces 50% of the world’s cork, thanks to the abundance of the native Cork Oak that covers 8% of the country’s total land area and makes up 28% of its forests.
The harvested cork is made into the wine stoppers we all know, but cork is also used to create flooring, furniture, a variety of household items, and has even broken into the fashion industry in the form of clothing and accessories. Across Portugal, (where the Cork Oak is the National Tree), you’ll find locals sporting cork backpacks, wallets, sandals, and belts, to name a few.
On a recent trip to the Douro Valley in northeastern Portugal, I was inspired by the locality of the wine-making process, exemplified by the roadside Cork Oaks whose harvested bark was used to plug the bottles of Portuguese wine made with grapes grown on the same hills.
The material is gaining more international recognition as a highly renewable and biodegradable resource that can replace traditional, more carbon intensive materials like wood, plastic, leather, and cotton in a wide variety of settings.
So what’s this tree all about?

Ecological Tenacity
The Cork Oak, or Quercus Suber, is an evergreen oak species native to the Mediterranean region, most commonly in Portugal, Spain, Italy, Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia. A lover of full sun, mild winters, and well-drained soil, the Cork Oak grows to a height of 40-70 feet. Its rounded crown consists of ovular, four-inch leaves that are dark green and leathery on top with a fuzzy, gray underside. The tree is characterized by its recognizable, fissured bark.
Cork Oaks are environmental stalwarts, working hard to prevent erosion and increasing the moisture level in the soil. These services are crucial: Cork Oaks are on the front lines as desertification creeps northward in Africa. These Mediterranean Forests are home to surprisingly biodiverse ecosystems with nearly 135 plant species per kilometer, including other oaks and wild olive trees. These forests shelter a wide variety of animal species and are final strongholds for crucially endangered species like the Iberian Lynx and Imperial Eagle. Their acorns serve as food for native birds and rodents, their yellow flowers feed pollinators, and their unique ability to regenerate their bark makes them a valuable resource for humans.
A Material of the Future?
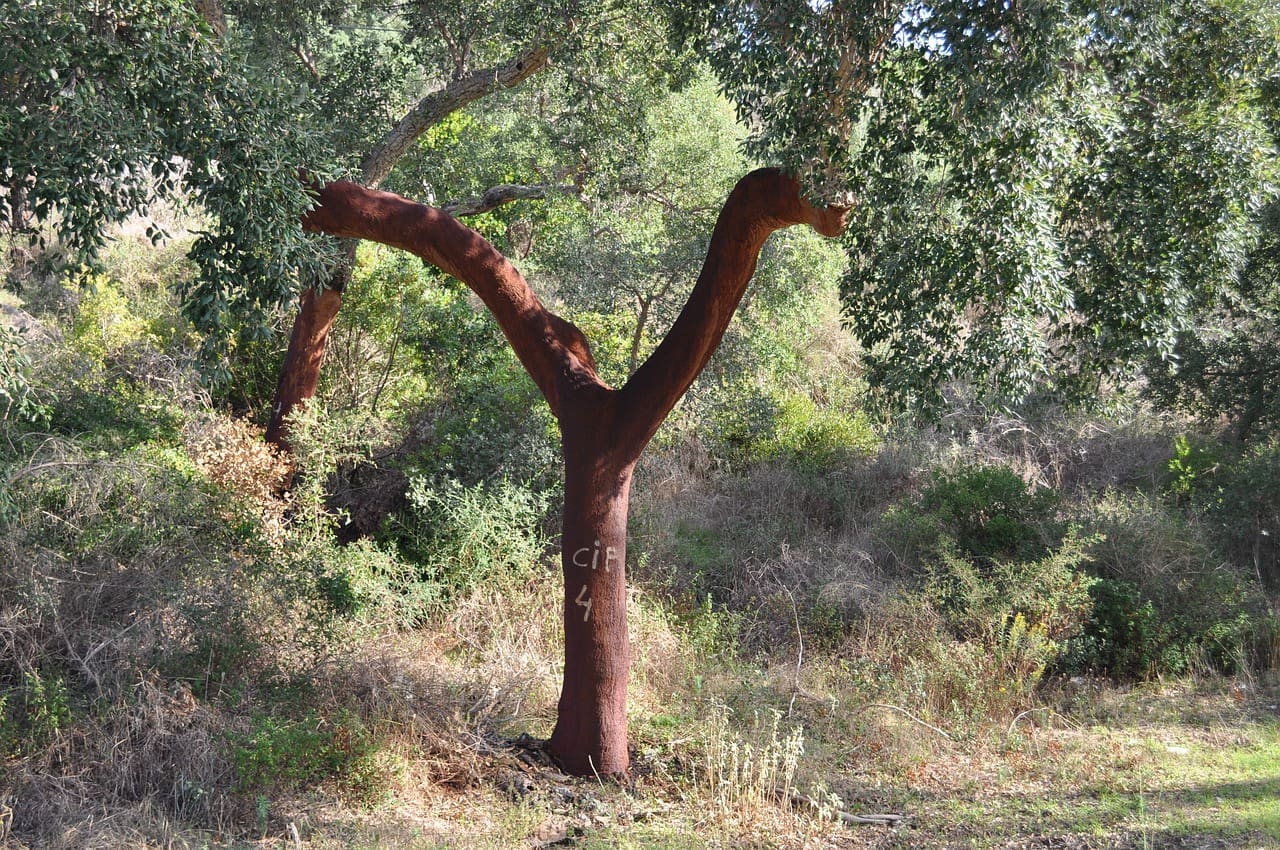
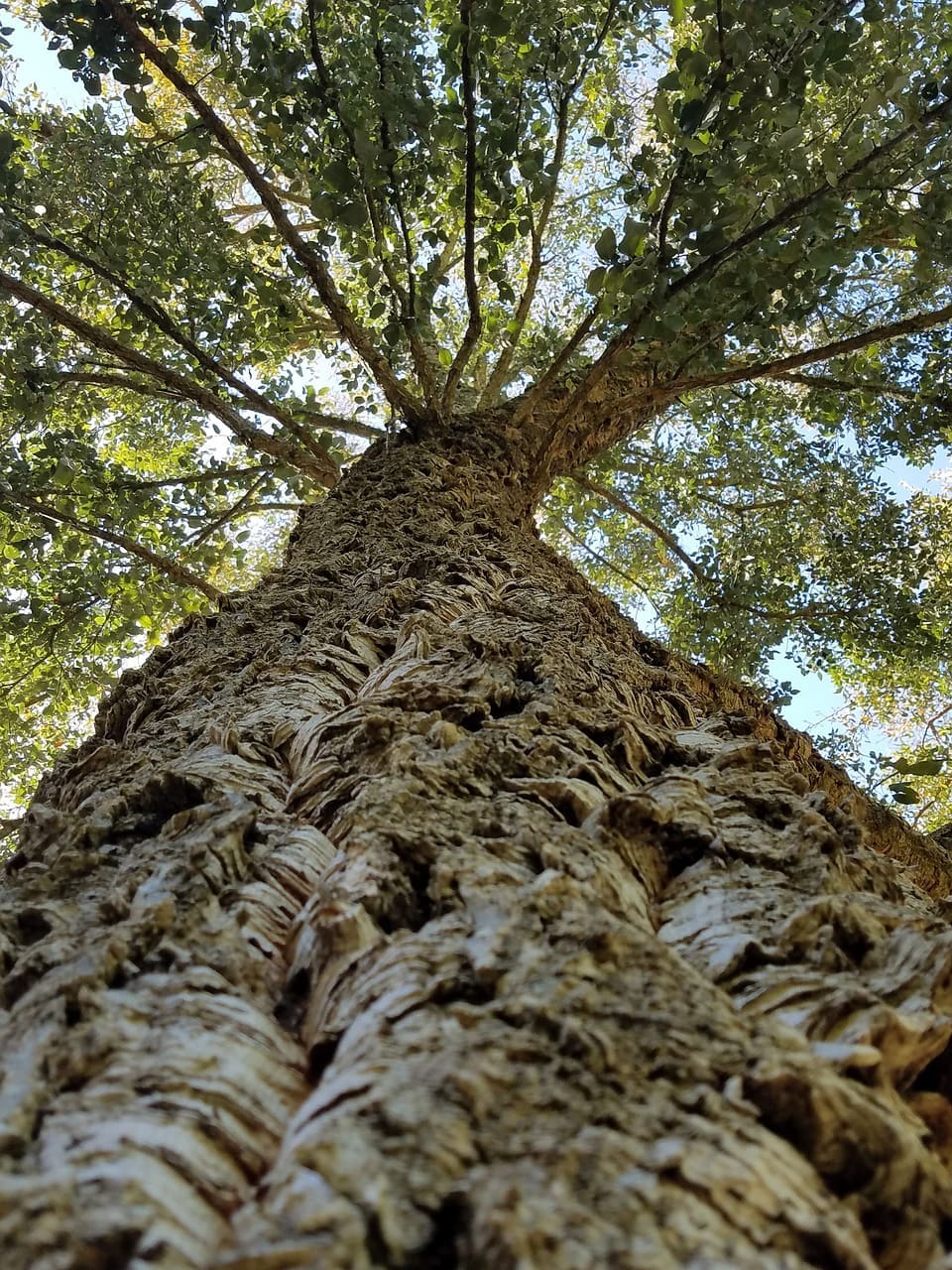
What sets Cork Oaks apart is their thick, fissured bark with the rare capacity to regenerate every 9-12 years. Its harvest is a heavily regulated process in Portugal that takes place between May and August each year. Laws allow the harvest of a single tree only once every nine years starting at age 25. The process leaves the tree standing, and allows time for the bark to regenerate completely between harvests. Large swaths of the outer bark is cut and peeled off by hand, exposing the tree’s striking, reddish-brown trunk. The last number of the harvest year is then marked on the tree in white paint, as seen below with a tree in the Douro Valley whose bark was harvested in 2023. This tree will be ready for another harvest in 2032, nine years later. With a lifespan of around 200 years, a single cork oak can be harvested up to 15 times!

(Douro Valley, Portugal)
Once the cork has been aged slightly, pressurized, and boiled (a six-month process), it becomes the lightweight and elastic material we find in our wine bottles. Naturally impervious to liquid while allowing a little air movement over time (this helps wine mature), the Ancient Greeks were the first to use cork as a bottle stopper over 2,000 years ago! It remains the preferred closure solution of contemporary winemakers.
With immense environmental and economic value, the Cork Oak is a unique species working hard to keep the deserts at bay and the wine drinkers happy. A protected species in Portugal since the 13th century, the ancient practice of cork bark harvesting is more important than ever. The tree is not harmed by this process; it actually helps it become a larger carbon sink. The photosynthesis required to regrow its bark results in additional carbon dioxide drawn down from the atmosphere after each harvest. This fascinating process is a rare win-win in the search for biodynamic and sustainable materials. How will we use it next?
So, the next time you celebrate a special occasion, share a bottle with friends, or enjoy a glass of Douro Valley Moscatel after dinner (something I recommend), take a moment to think about the wonderful uniqueness of the material at play. And don’t forget to compost those corks at the end of the night!
Off I pop!
Ryan

Ryan Pagois is a climate advocate and systems thinker serving as an Associate Director at Built Environment Plus, helping to drive sustainable building solutions in MA. He is passionate about urban ecology, carbon balance, and rewilding cities. He is excited to pursue a Masters of Ecological Design at the Conway School starting this fall, to explore how low-impact urban development can be our greatest climate solution and community resilience tool. He grew up in Minnesota and studied environmental policy and international relations at Boston University.
Sources and Further Reading:
https://www.rainforest-alliance.org/species/cork-oak
https://www.gardenia.net/plant/quercus-suber
https://cycling-centuries.com/blogs/news/everything-you-could-ever-want-to-know-about-cork-trees
https://www.bourrasse.com/en/the-history-of-the-cork-closure