Creature Taxonomy Manager
All Terms
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Amphibians | Cold-blooded vertebrates that live both in water and on land, including frogs, salamanders, and newts. |
| Birds | Creatures with feathers, wings, and the ability to lay eggs, many of which can fly. |
| Burrowing Animals | |
| Condensation Microbes | Microorganisms that influence cloud formation and condensation processes, linking with atmospheric research. |
| Cooling | The role of plant transpiration in shedding heat to space via the small water cycle (transpiration -> clouds -> rain -> infiltration). |
| Cover Crops | Plants like clover, rye, or legumes that protect and enrich soil, reduce erosion, and support microbial diversity. |
| Croplands | Agricultural areas producing food, with potential for regenerative practices to enhance soil health and biodiversity. |
| Decay Wizards | Species like fungi, bacteria, and detritivores that break down organic material, returning nutrients to the soil. |
| Desert Dwellers | Creatures that have adapted to live in arid and dry desert environments. |
| Ecosystem Engineers | Creatures that drastically alter environments, such as beavers, corals, elephants, or wolves. |
| Endangered Species | Creatures at risk of extinction due to habitat loss, hunting, or other environmental pressures. |
| Environmental Monitors/BioIndicators | Species like frogs and lichens that reveal environmental health through their presence or absence. |
| Filter Feeders | Organisms like oysters that filter particulates from water, improving clarity and ecosystem health. |
| Forest Inhabitants | Creatures that thrive in forest ecosystems, from birds to mammals to insects. |
| Forests | Ecosystems rich in biodiversity, acting as carbon sinks and critical habitats for countless species. |
| Fungi | A group of spore-producing organisms feeding on organic matter, including molds, yeast, and mushrooms. |
| Grassland Inhabitants | |
| Grasslands | Ecosystems dominated by grasses, supporting grazing animals and acting as carbon reservoirs. |
| Grazers | Grazing animals like cows, sheep, and goats, converting plant biomass into meat and bioactivated fertilizer that enriches soil. |
| Infiltration Team | Creatures or organisms that help water penetrate the soil, such as earthworms and burrowing animals like prairie dogs. |
| Insects | Small, air-breathing arthropods with six legs, often having wings. |
| Intelligent Creatures | |
| Invasive Species | |
| Keystone Species | Species with a disproportionately large effect on ecosystems, like sea otters or elephants, often also ecosystem engineers. |
| Living Shorelines | Coastal ecosystems that protect against erosion and support marine biodiversity through natural barriers like seagrass and oyster reefs. |
| Mammals | Warm-blooded animals with hair or fur, most of which give birth to live young. |
| Marine Life | Creatures that primarily inhabit oceans, seas, and other saltwater environments. |
| Maximizing Photosynthesis | Highly efficient photosynthesizers like cyanobacteria, seagrasses, and algae that sequester carbon and produce oxygen. |
| Medicinal Organisms | |
| Mother Tree Networks | Trees like Douglas fir that act as central hubs, sharing resources via underground mycorrhizal networks. |
| Mycelium Connections | Mycorrhizal fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plants, facilitating nutrient and water exchange. |
| Pest Controllers | |
| Pioneer Species | Species that are the first to colonize barren or disturbed environments, facilitating ecological succession and habitat restoration. |
| Plants | Photosynthetic organisms that form the base of most ecosystems and provide food and shelter for various creatures. |
| Pollinators | Diverse pollinators such as bees, butterflies, bats, and wind-pollinating plants, playing a critical role in food production and plant biodiversity. |
| Rapid Growers | |
| Reptiles | Cold-blooded, scale-covered animals that typically lay eggs and are well-adapted to diverse environments. |
| Scavenger | Organisms that feed on dead or decaying organic matter, playing a crucial role in nutrient recycling and ecosystem health. |
| Soil Sponge | Organisms like fungi and plant roots that build soil structure and enhance water retention. |
| Top Predators | Animals like wolves, sharks, and eagles that regulate populations, maintaining balance within ecosystems. |
| Transpiration Champions | Trees that release water vapor through transpiration, contributing to local and global water cycles. |
| Unique Adaptations | Creatures that have developed specialized adaptations for survival, behavior, or reproduction. |
| Urban Wildlife | |
| Venomous Creatures | Creatures that use venom as a defense mechanism or for subduing prey. |
| Water Quality Team | Creatures that maintain clean water, like freshwater mussels or beavers, which create wetlands that filter pollutants. |
| Wetlands | Vital ecosystems that support biodiversity, filter water, and protect against flooding. |
-
Featured Creature: Markhor

-
Featured Creature: Coast Redwood

-
Featured Creature: Earthworms

-
Featured Creature: Axolotl

-
Featured Creature: Giant Squirrels of India

-
Featured Creature: African grey parrot

-
Featured Creature: Giraffes

-
Featured Creature: Macrotermes Termites

-
Featured Creature: European Starling

-
Featured Creature: Rotifers

-
Featured Creature: Penguins

-
Featured Creature: Prickly Pear Cactus

-
Featured Creature: Mexican Wolf

-
Featured Creature: Pika

-
Featured Creature: Sloth

-
Featured Creature: Japanese Knotweed

-
Featured Creature: Cicada

-
Featured Creature: Seahorse

-
Featured Creature: Yucca

-
Featured Creature: Staghorn sumac

-
Featured Creature: Lavender

-
Featured Creature: Kingfisher

-
Featured Creature: Strangler Fig

-
Featured Creature: ‘Ōhi’a Lehua

-
Featured Creature: Stone Pine

-
Featured Creature: Sphagnum moss

-
Featured Creature: Mouse-ear cress

-
Featured Creature: Red kite

-
Featured Creature: Cheatgrass

-
Featured Creature: Moon Snail

-
Featured Creature: Slow Loris

-
Featured Creature: Iberian Hare

-
Featured Creature: Eastern Emerald Elysia

-
Featured Creature: Leafcutter Bee

-
Featured Creature: Coelacanth

-
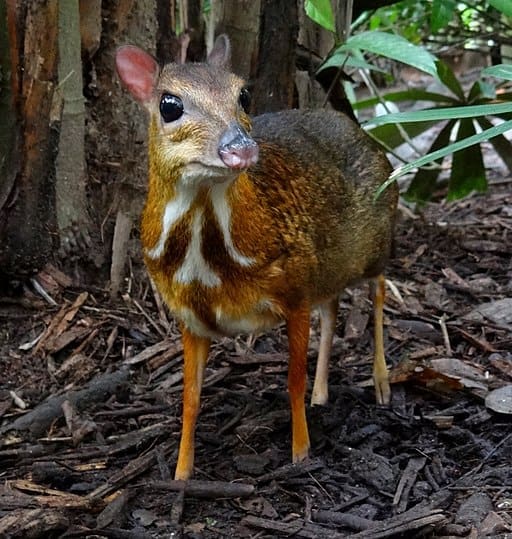
Featured Creature: Chevrotain

-
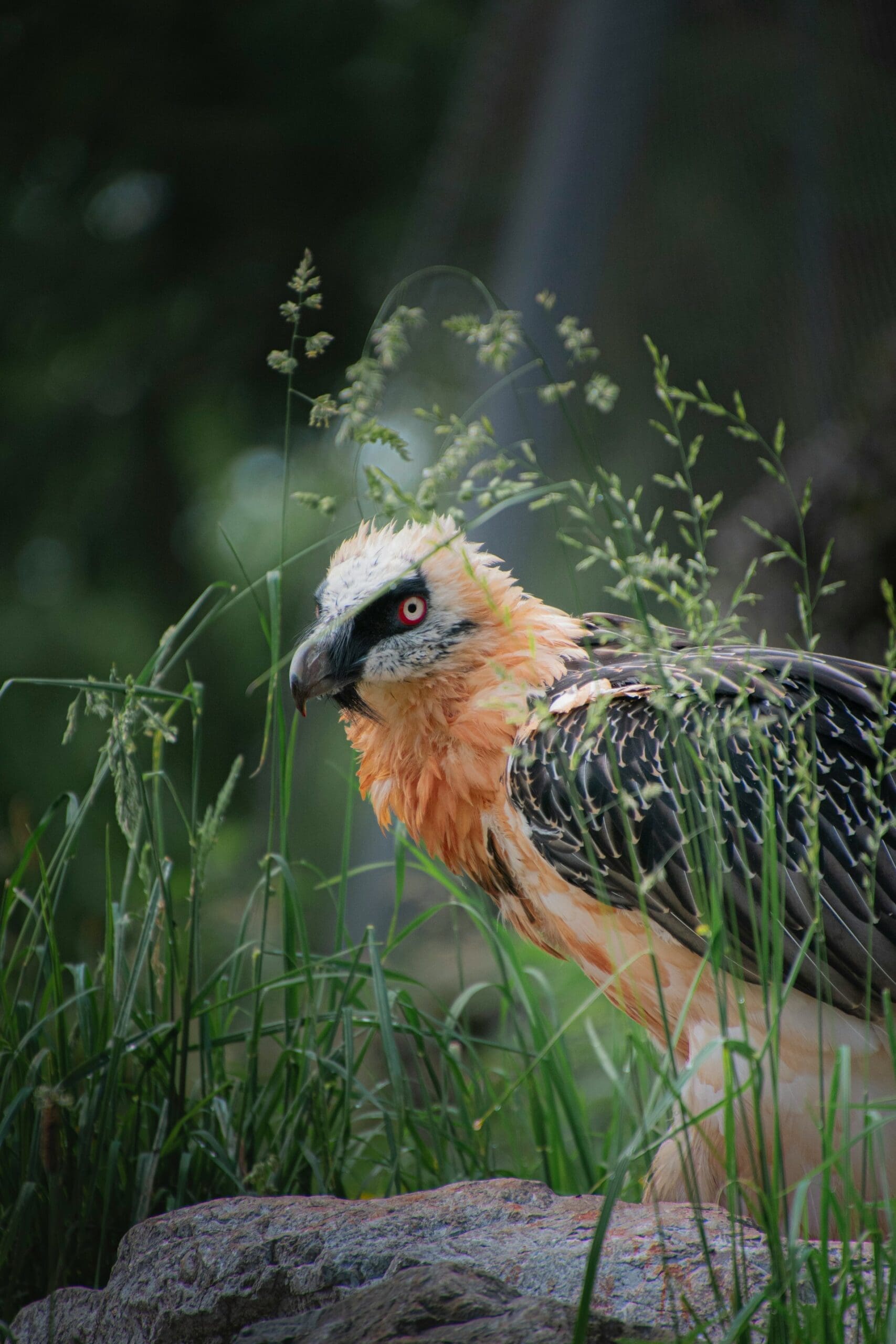
Featured Creature: Bearded Vulture

-
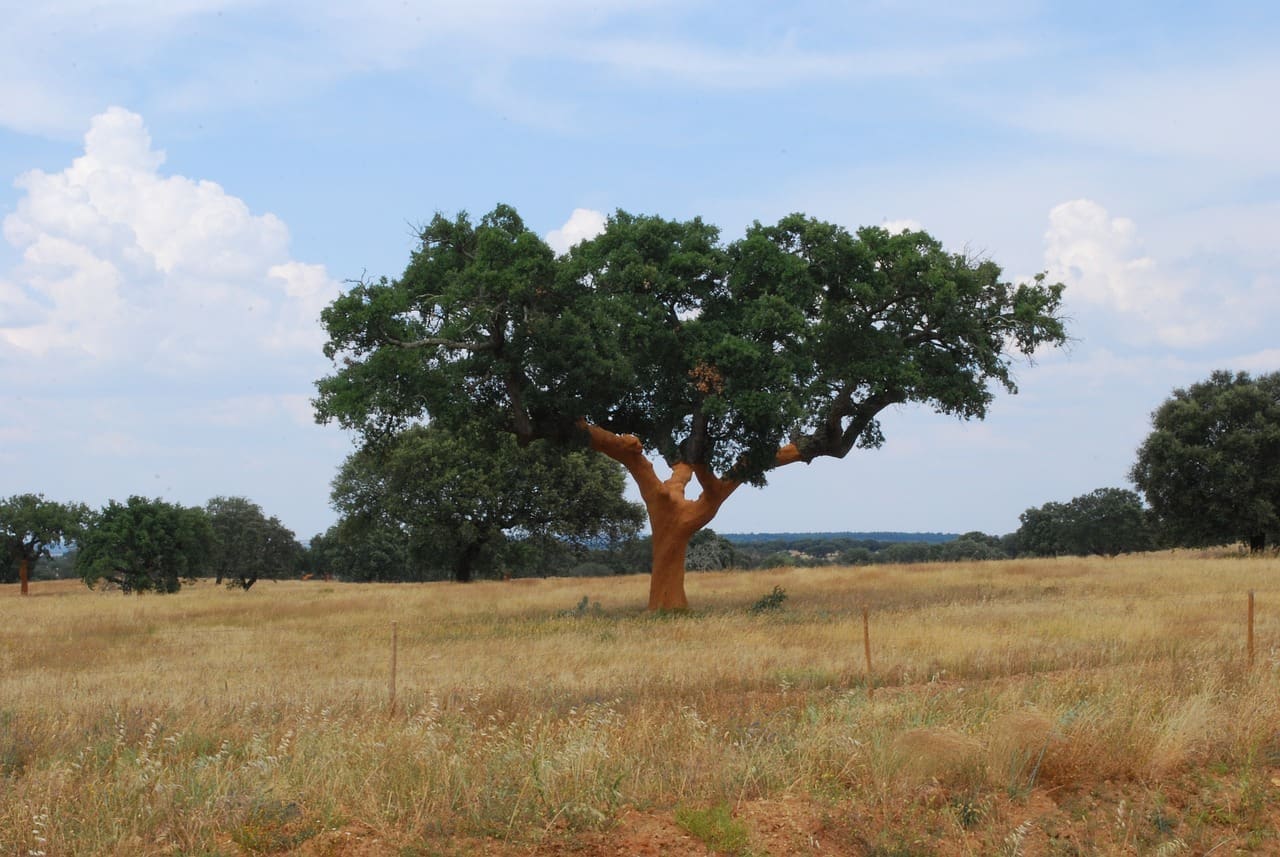
Featured Creature: Cork Oak

-
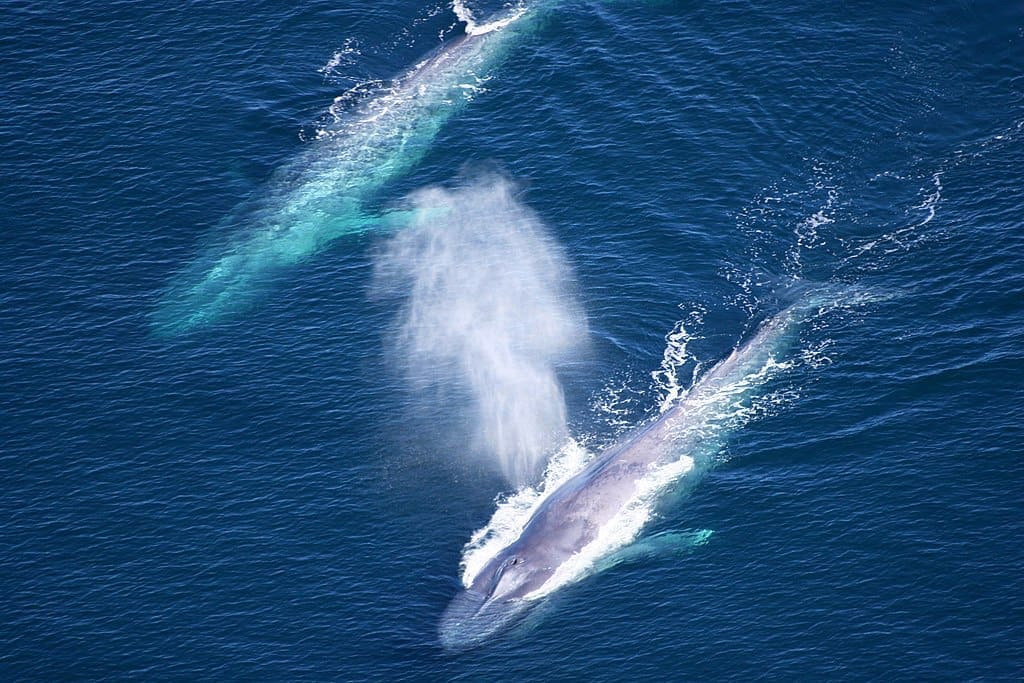
Featured Creature: Blue Whale

-
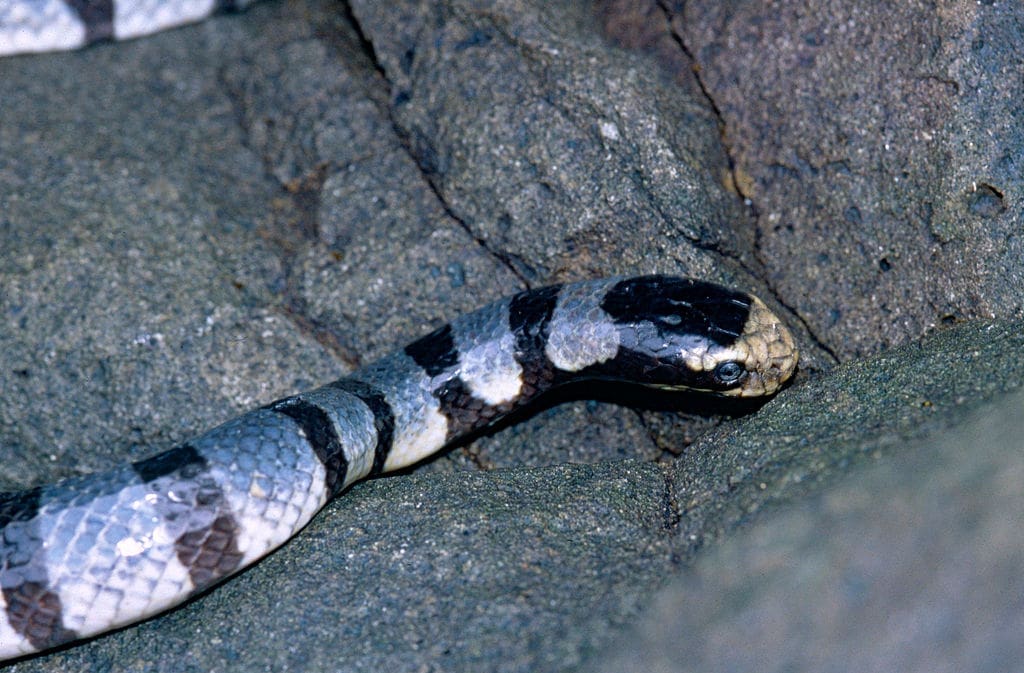
Featured Creature: Banded Sea Krait

-
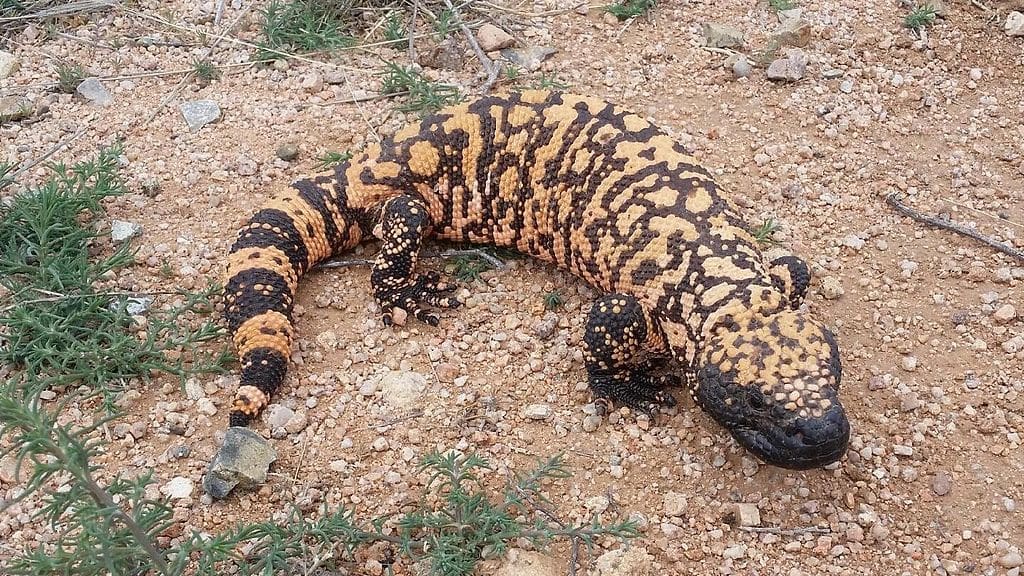
Featured Creature: Gila Monster

-
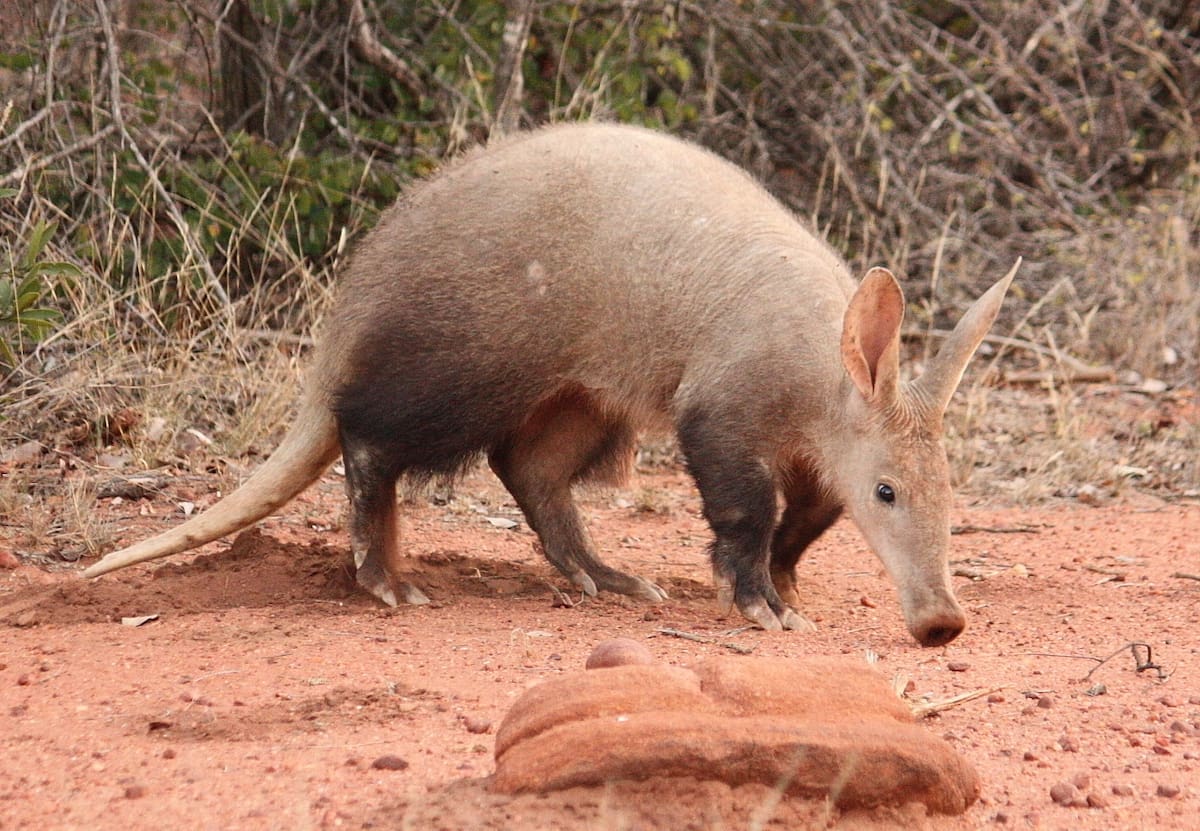
Featured Creature: Aardvark

-
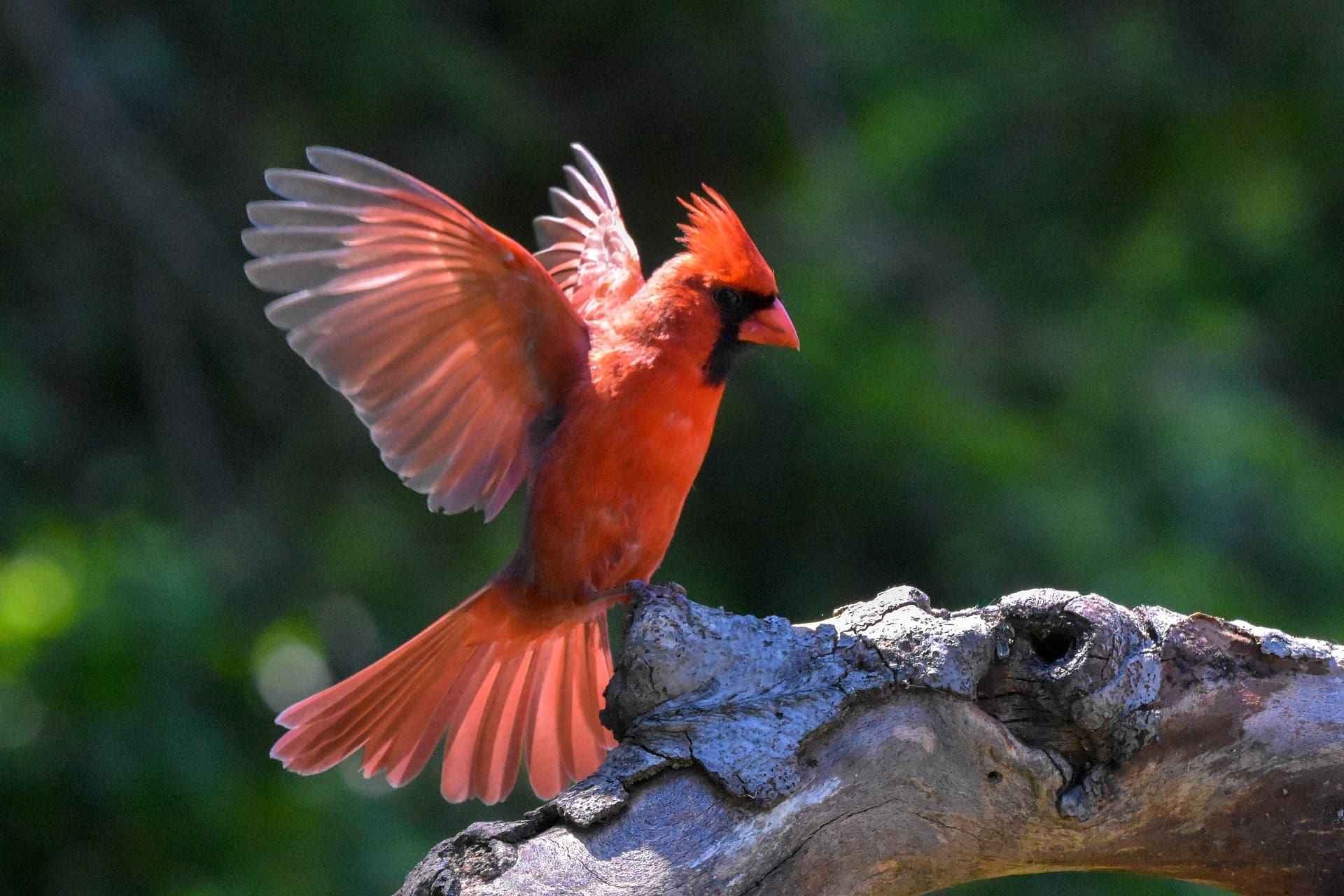
Featured Creature: Northern Cardinal

-
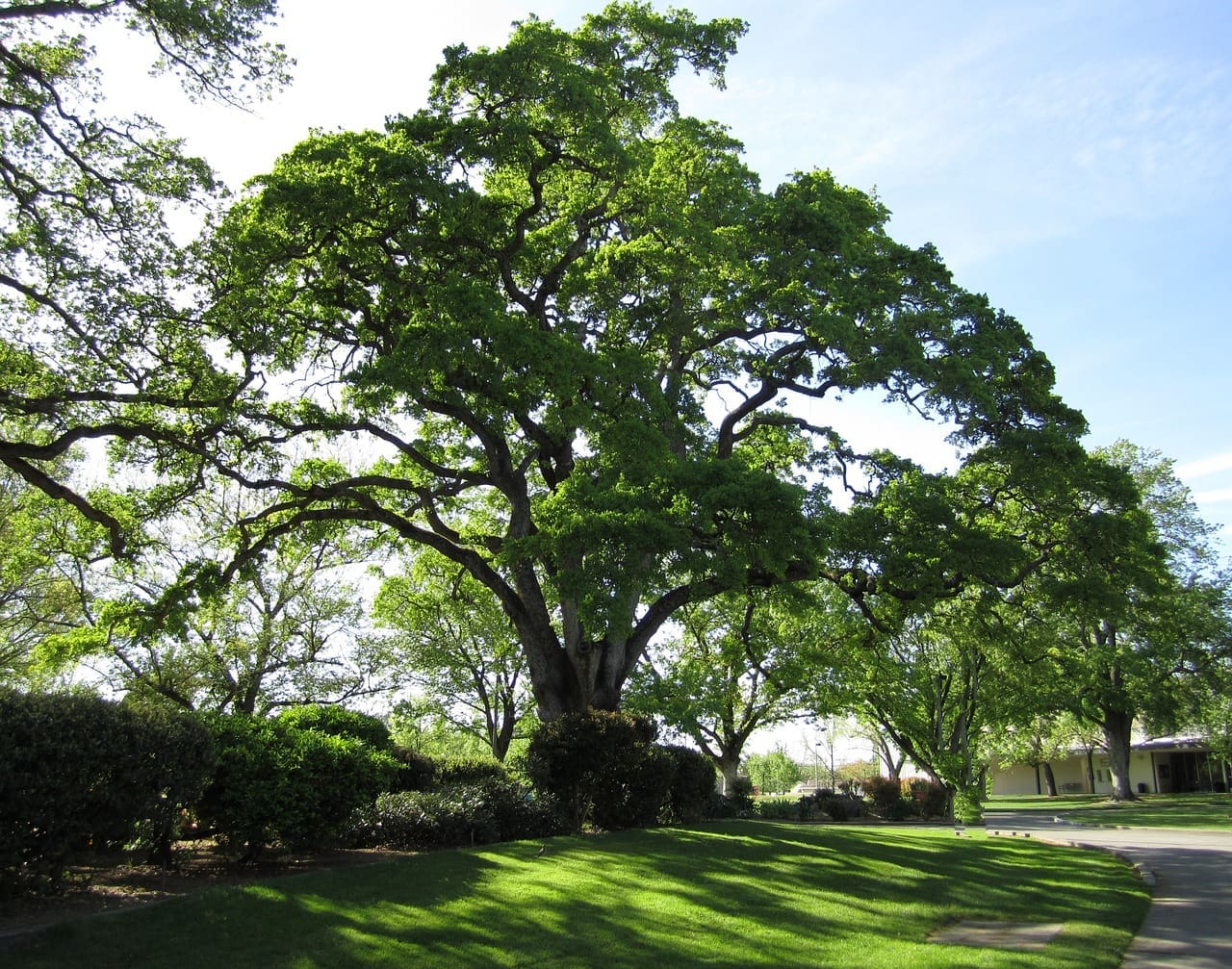
Featured Creature: Northern Red Oak

-
Featured Creature: Cat

-
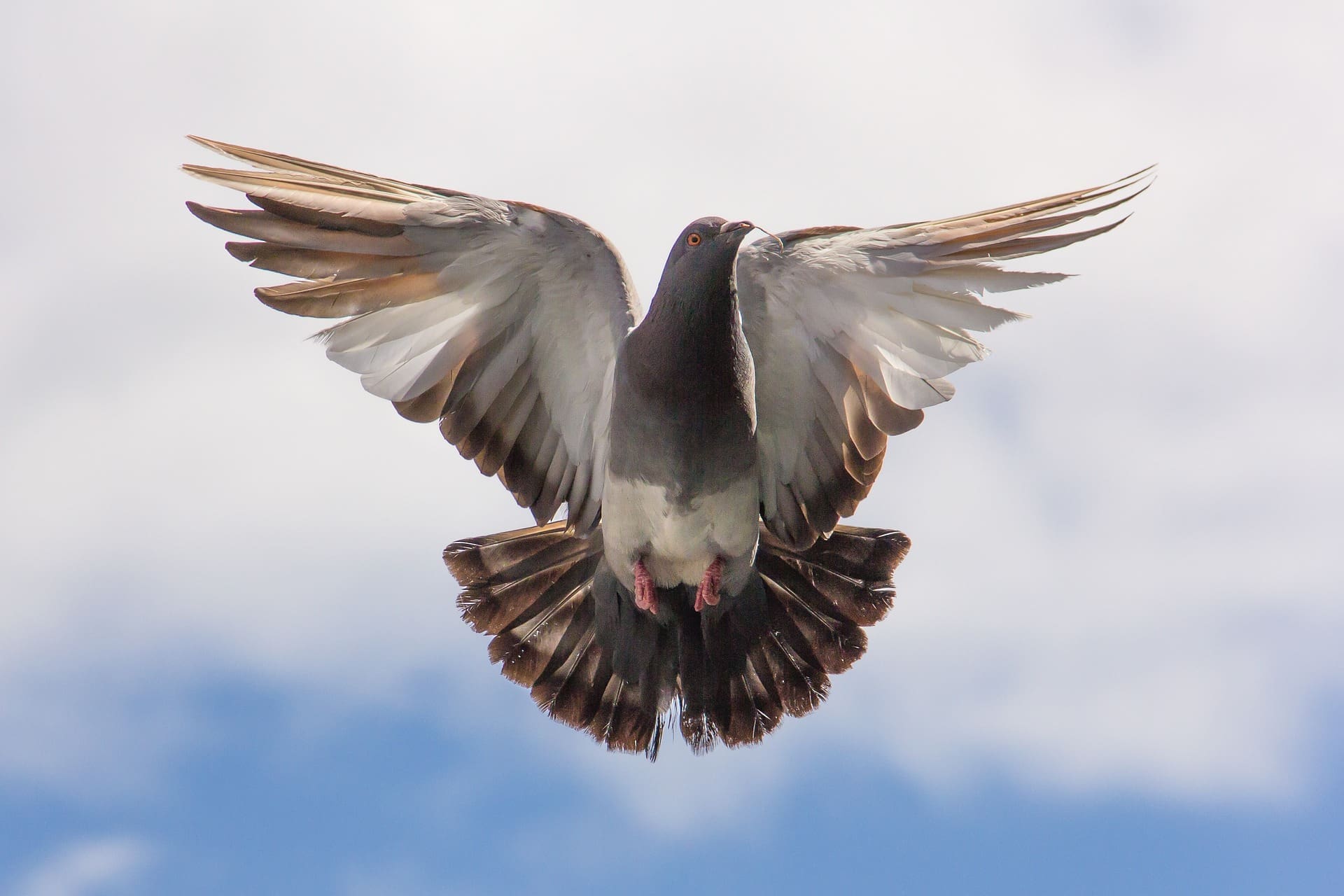
Featured Creature: Pigeon

-
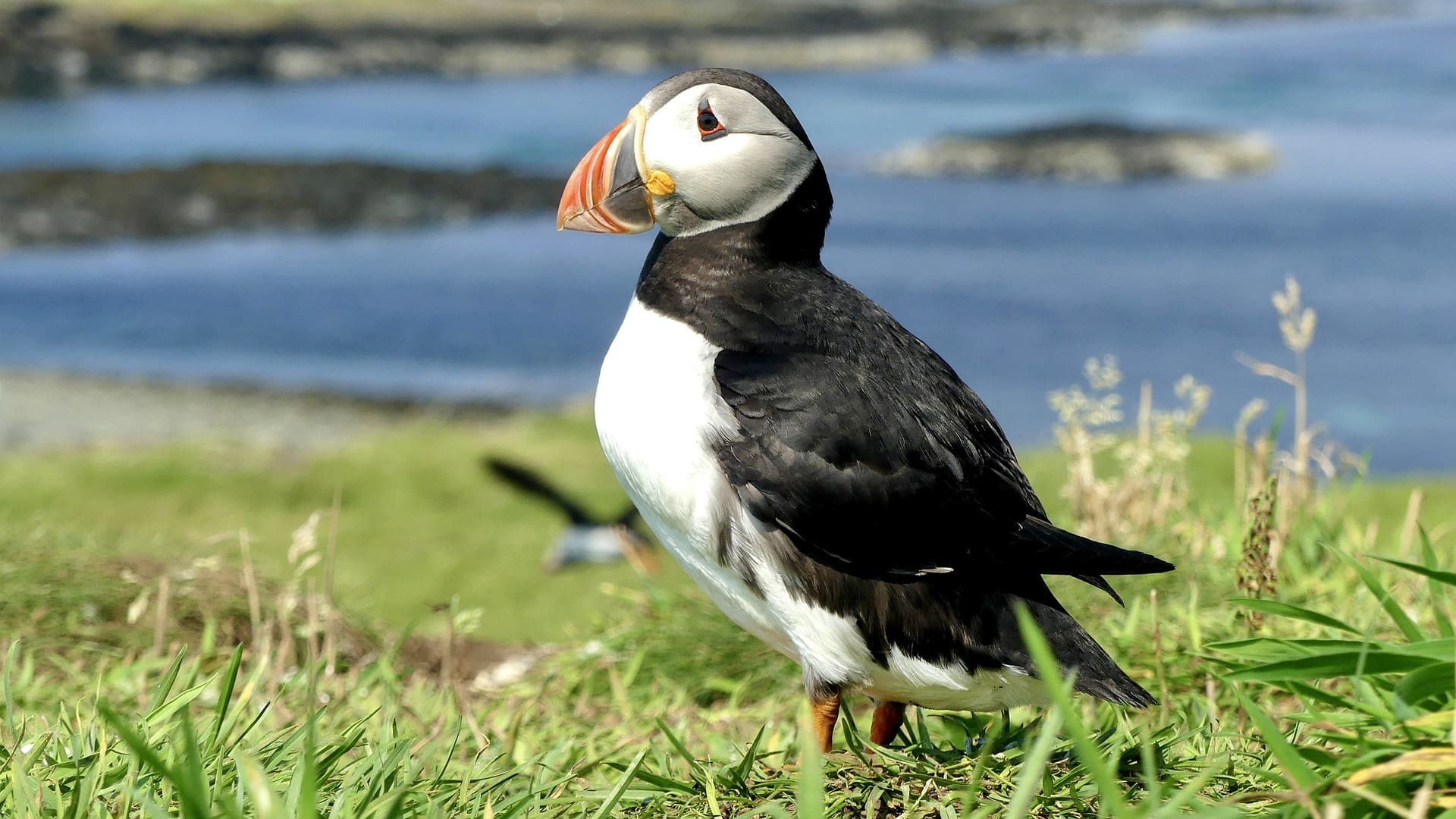
Featured Creature: Atlantic Puffin

-
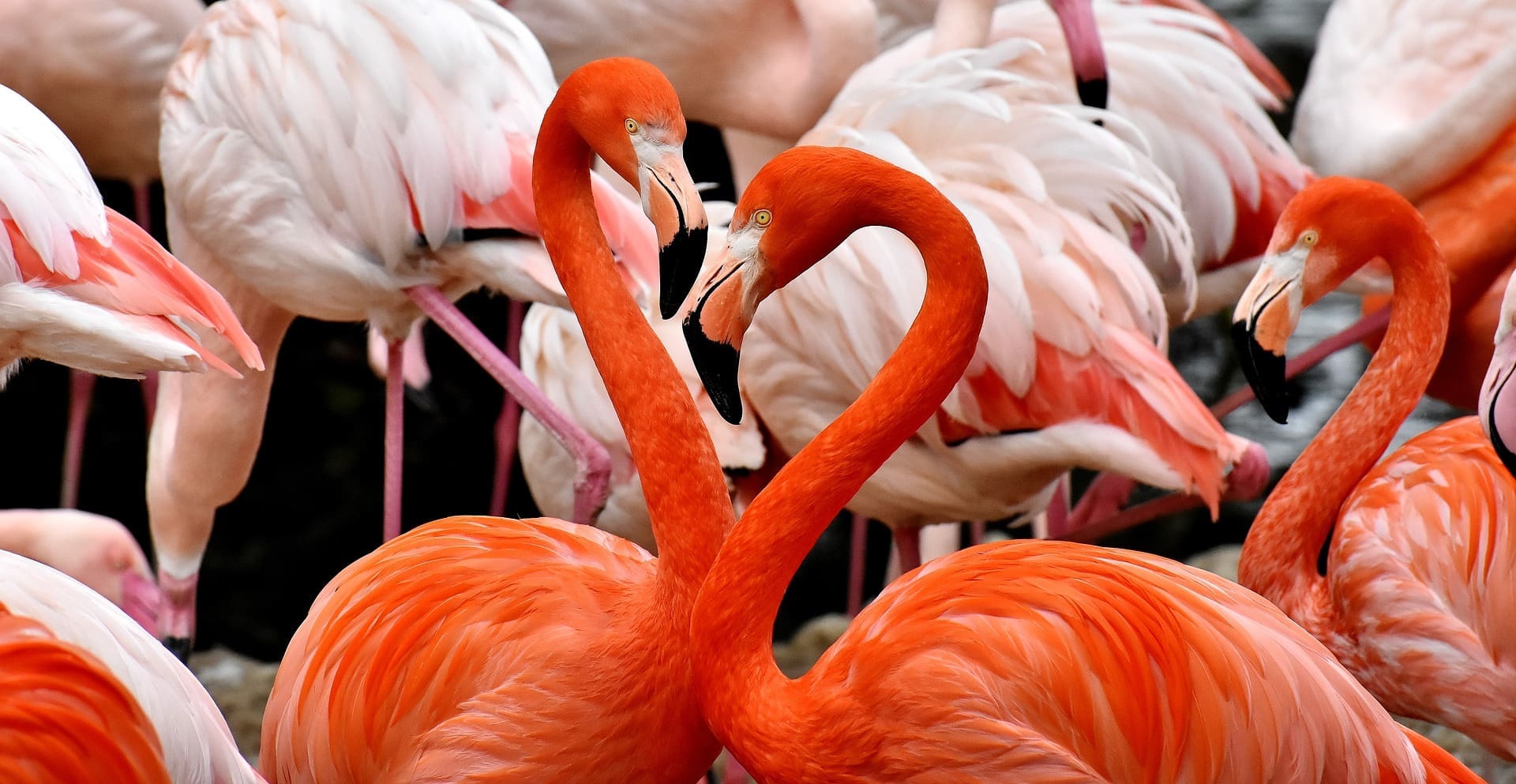
Featured Creature: Flamingo

-
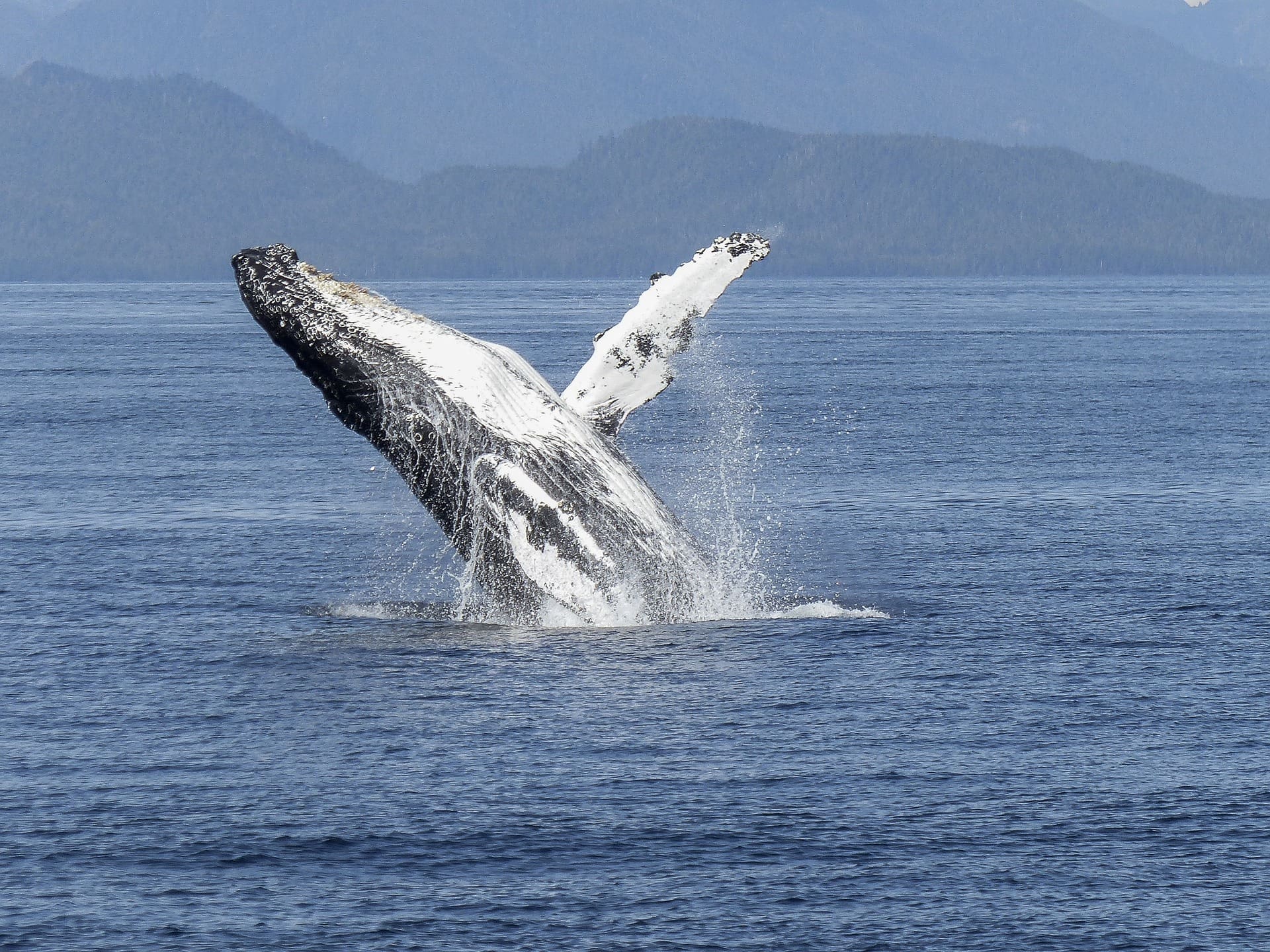
Featured Creature: Humpback Whale

-
Featured Creature: Groundhog

-
Featured Creature: Crow

-
Featured Creature: Canada Lynx

-
Featured Creature: Fishing Cat

-
Featured Creature: American Chestnut

-
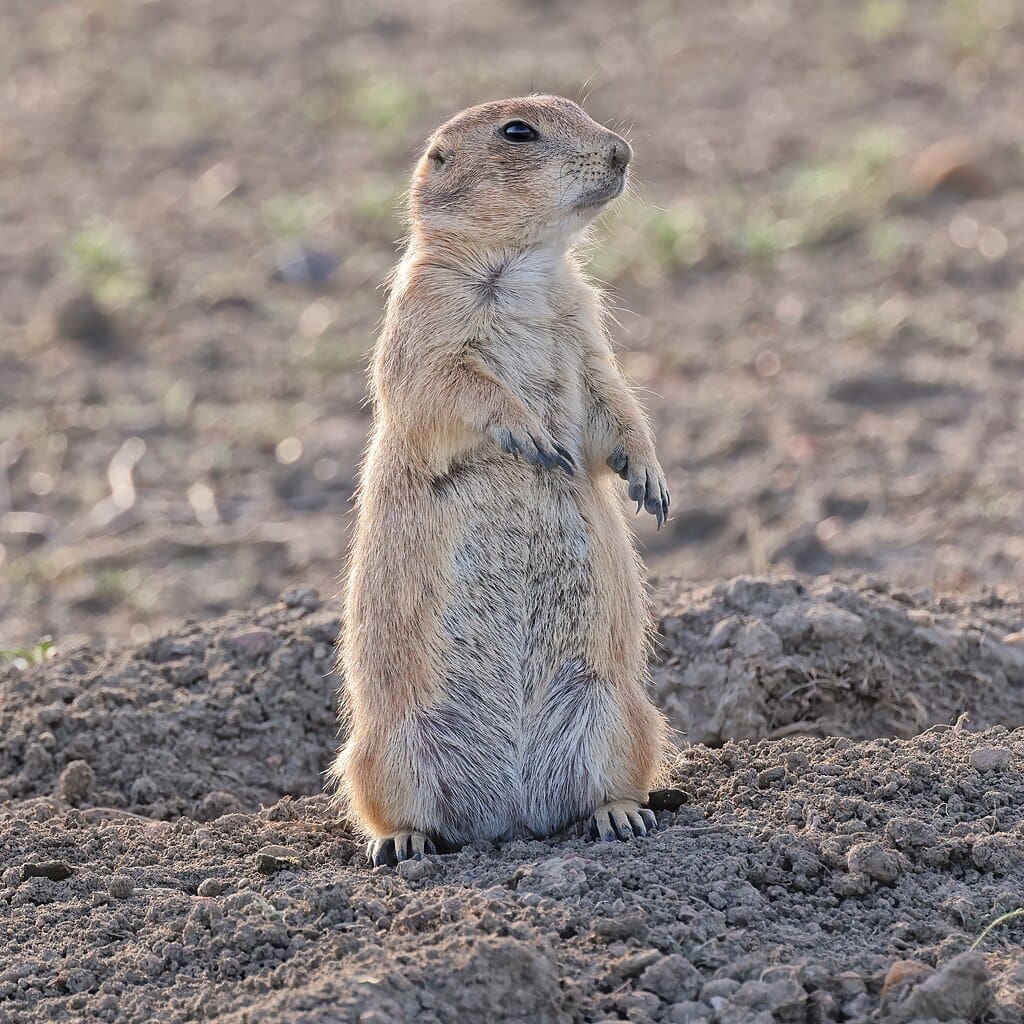
Featured Creature: Prairie Dog

-
Featured Creature: Bamboo

-
Featured Creature: Pando

-
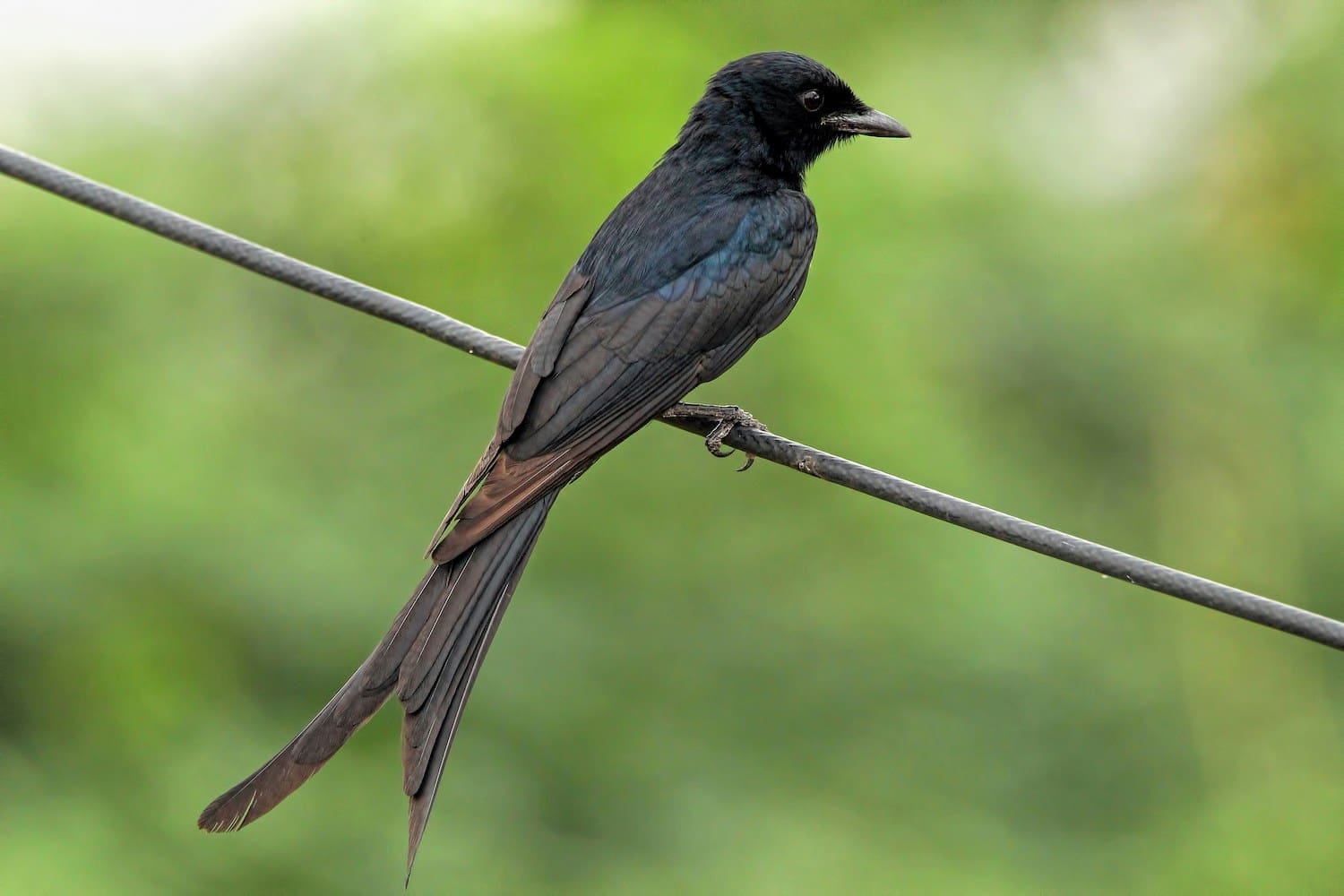
Featured Creature: Black Drongo

-
Featured Creature: Zombie Ant Fungus

-
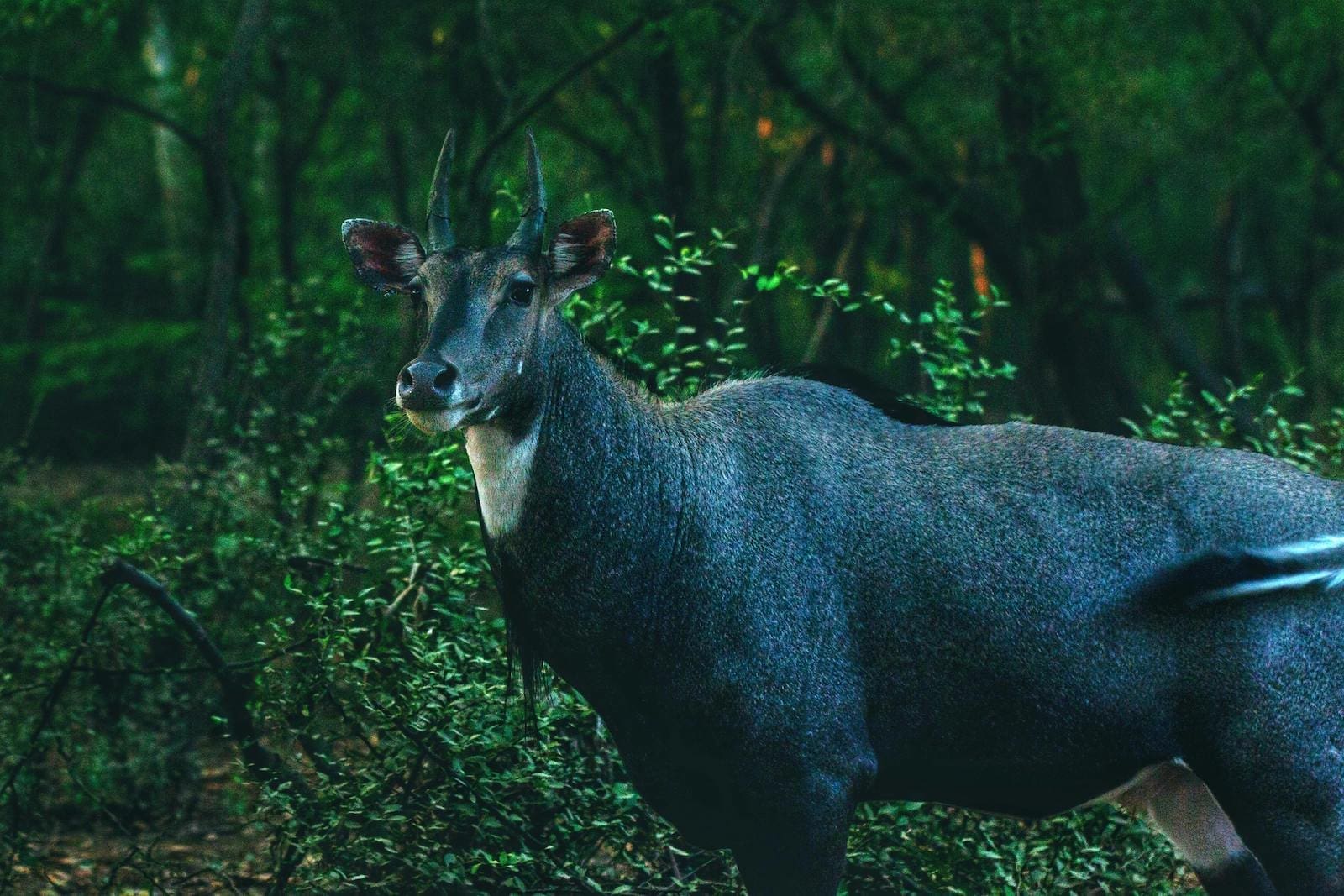
Featured Creature: Nilgai

-
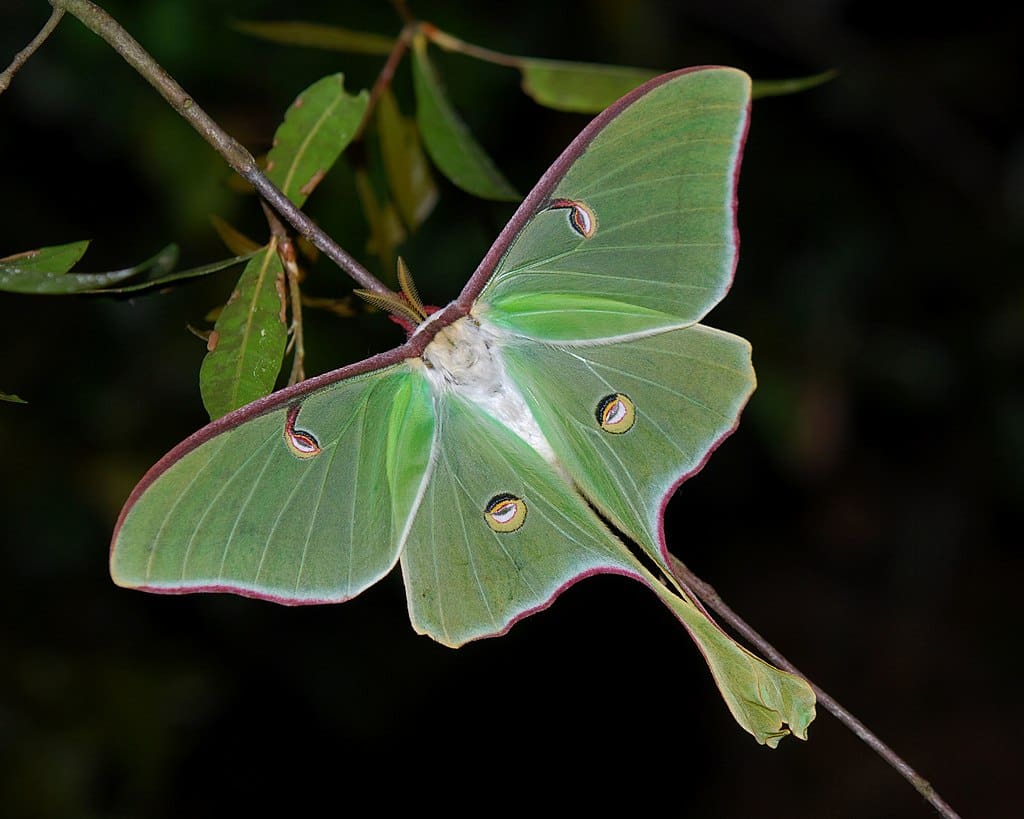
Featured Creature: Luna Moths

-
Featured Creature: Beaver

-
Featured Creature: Asian Giant Hornet

-
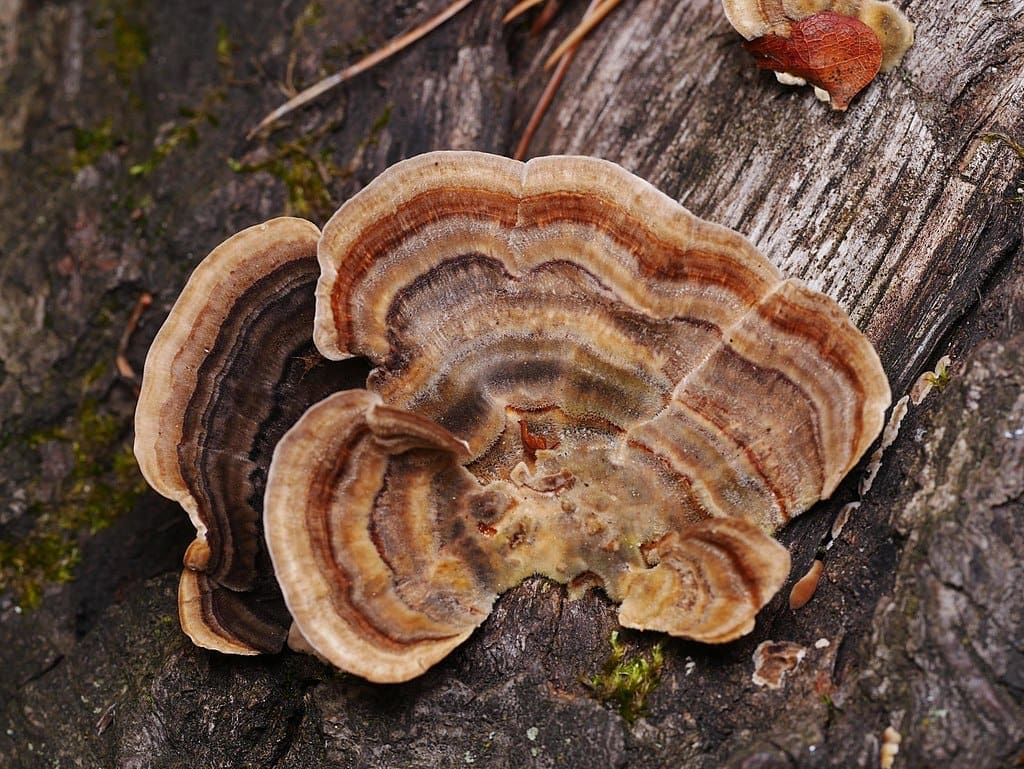
Featured Creature: Turkey Tails

-
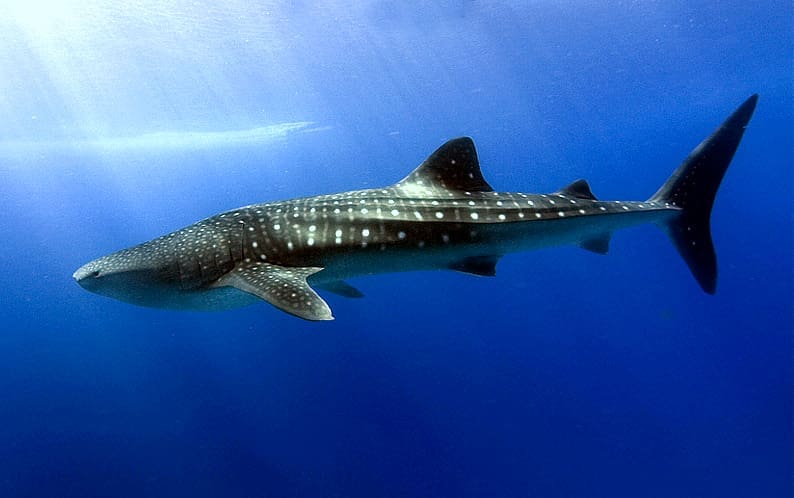
Featured Creature: Whale Shark

-
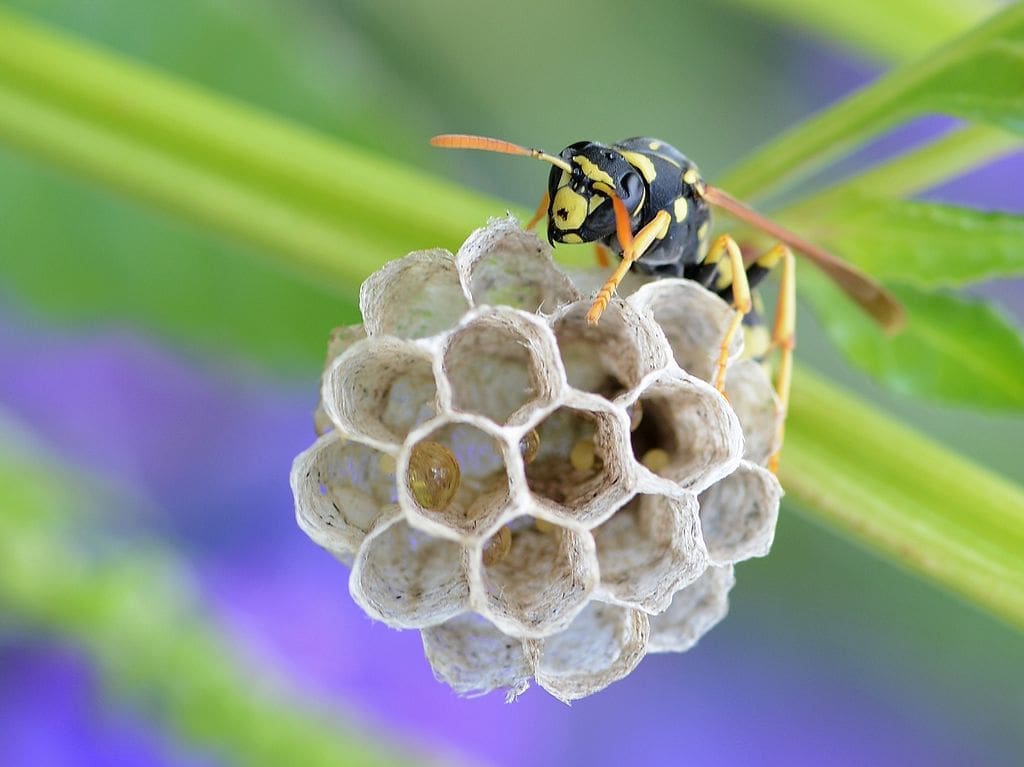
Featured Creature: Wasps

-
Featured Creature: European Hamster

-
Featured Creature: Banded Mongoose

-
Featured Creature: Lichen

-
Featured Creature: Clamworm

-
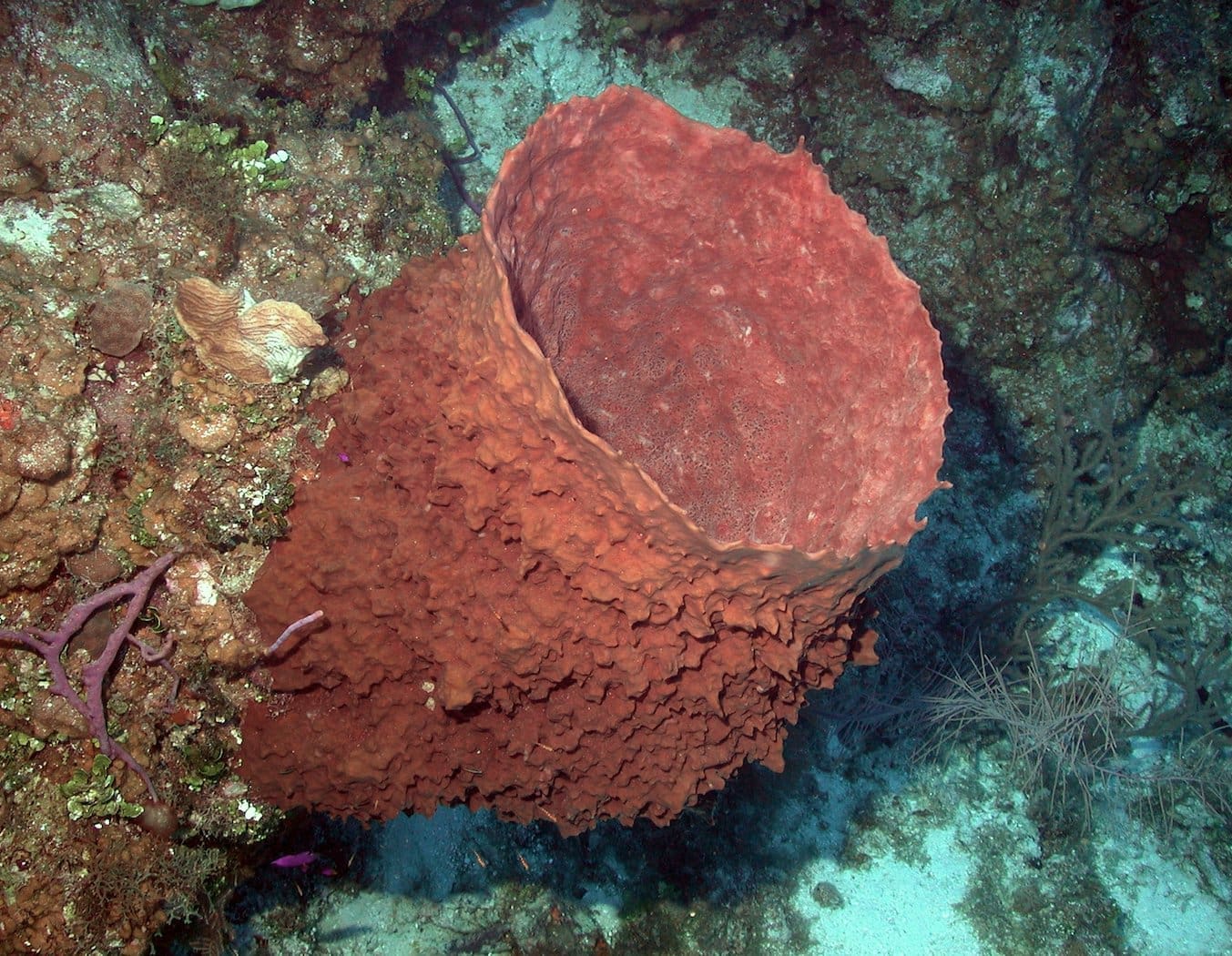
Featured Creature: Giant Barrel Sponge

-
Featured Creature: Ladybug

-
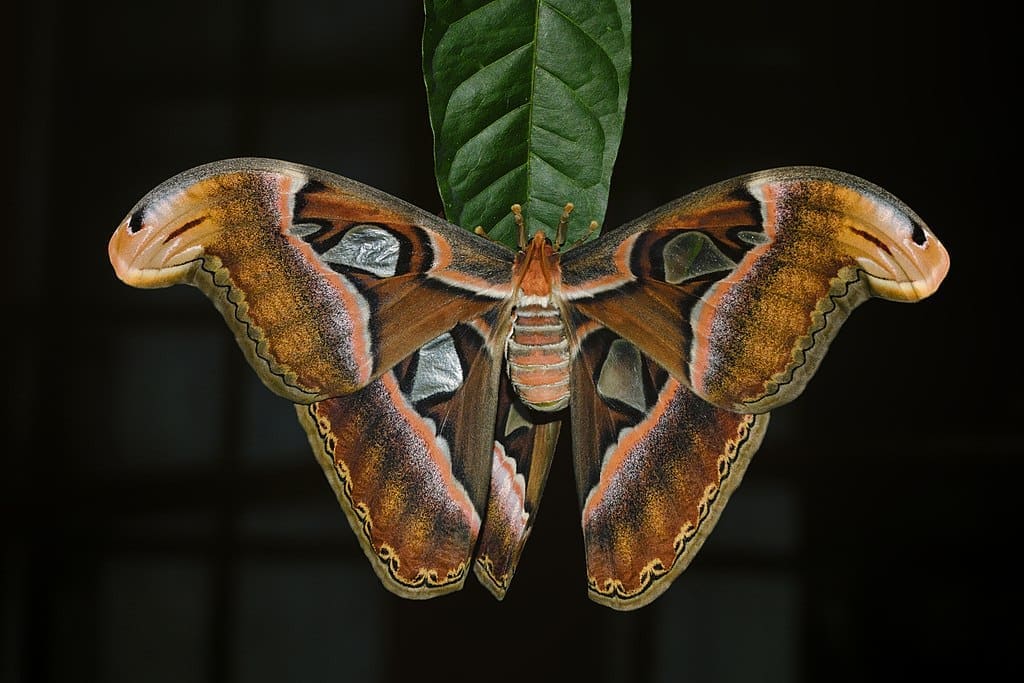
Featured Creature: Atlas Moth

-
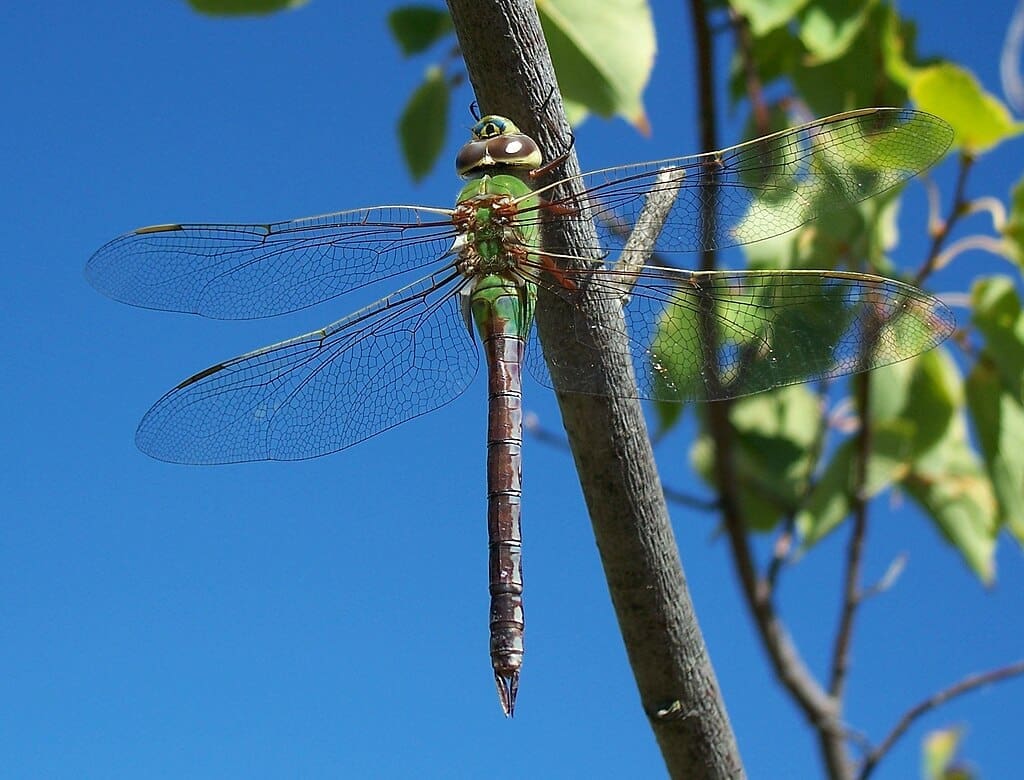
Featured Creature: Dragonfly

-
Featured Creature: Slime Mold

-
Featured Creature: Poison Dart Frog

-
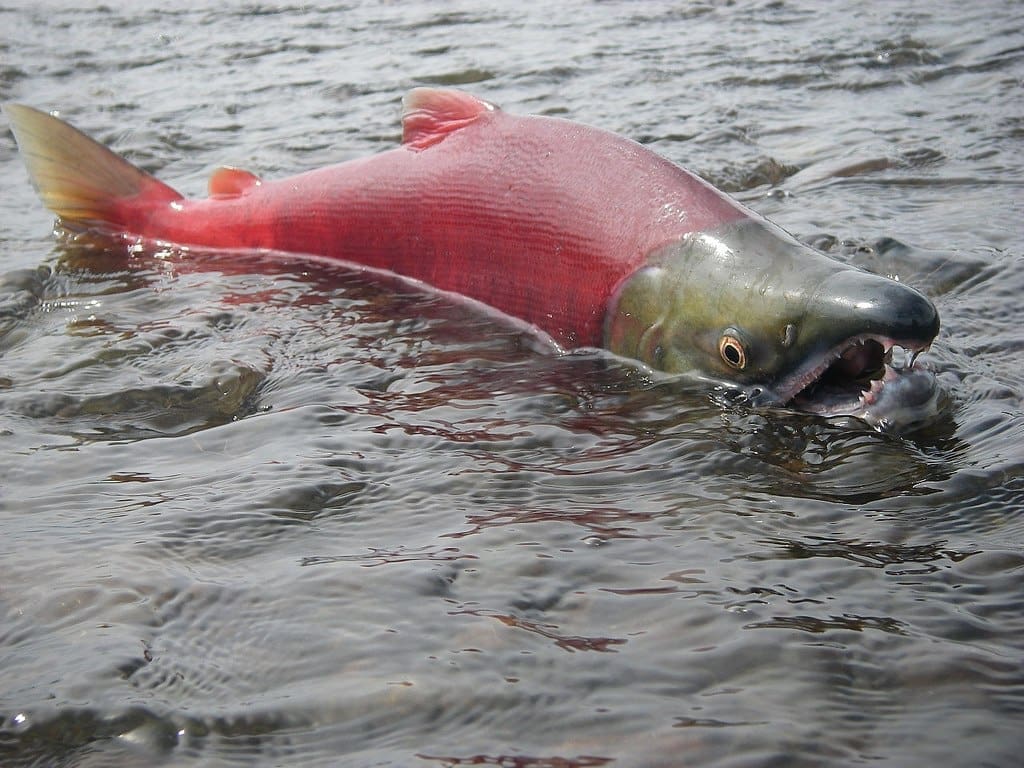
Featured Creature: Pacific Salmon